Federal Circuit Affirms Alice Nix of Poll-Based Networking System
| August 10, 2023
Trinity Info Media v Covalent, Inc.
Decided: July 14, 2023
Before Stoll, Bryson and Cunningham.
Summary:
The Federal Circuit affirmed patent ineligibility of the Trinity’s poll-based networking system under Alice. The claims are directed to the abstract idea of matching based on questioning, something that a human can do. The additional features of a data processing system, computer system, web server, processor(s), memory, hand-held device, mobile phone, etc. are all generic components providing a technical environment for performing the abstract idea and do not detract from the focus of the claims being on the abstract idea. The specification also does not support a finding that the claims are directed to a technological improvement in computers, mobile phones, computer systems, etc.
Procedural History:
Trinity sued Covalent for infringing US Patent Nos. 9,087,321 and 10,936,685 in 2021. The district court granted Covalent’s 12(b)(6) motion to dismiss, concluding that the asserted claims are not patent eligible subject matter under 35 USC §101. Trinity appealed.
Decision:
Representative claim 1 from the ‘321 patent is as follows:
A poll-based networking system, comprising:
a data processing system having one or more processors and a memory, the memory being specifically encoded with instructions such that when executed, the instructions cause the one or more processors to perform operations of:
receiving user information from a user to generate a unique user profile for the user;
providing the user a first polling question, the first polling question having a finite set of answers and a unique identification;
receiving and storing a selected answer for the first polling question;
comparing the selected answer against the selected answers of other users, based on the unique identification, to generate a likelihood of match between the user and each of the other users; and
displaying to the user the user profiles of other users that have a likelihood of match within a predetermined threshold.
Representative claim 2 from the ‘685 patent is as follows:
A computer-implemented method for creating a poll-based network, the method comprising an act of causing one or more processors having an associated memory specifically encoded with computer executable instruction means to execute the instruction means to cause the one or more processors to collectively perform operations of:
receiving user information from a user to generate a unique user profile for the user;
providing the user one or more polling questions, the one or more polling ques-tions having a finite set of answers and a unique identification;
receiving and storing a selected answer for the one or more polling questions;
comparing the selected answer against the selected answers of other users, based on the unique identification, to generate a likelihood of match between the user and each of the other users;
causing to be displayed to the user other users, that have a likelihood of match within a predetermined threshold;
wherein one or more of the operations are carried out on a hand-held device; and
wherein two or more results based on the likelihood of match are displayed in a list reviewable by swiping from one result to another.
Looking at the claims first, the claimed functions of (1) receiving user information; (2) providing a polling question; (3) receiving and storing an answer; (4) comparing that answer to generate a “likelihood of match” with other users; and (5) displaying certain user profiles based on that likelihood are all merely collecting information, analyzing it, and displaying certain results which fall in the “familiar class of claims ‘directed to’ a patent ineligible concept,” which a human mind could perform. The court agreed with the district court’s finding that these claims are directed to an abstract idea of matching based on questioning.
The ‘685 patent adds the further function of reviewing matches using swiping and a handheld device. These features did not alter the court’s decision. The dependent claims also added other functional variations, such as performing matching based on gender, varying the number of questions asked, displaying other users’ answers, etc. These are all trivial variations that are themselves abstract ideas. The further recitation of the hand-held device, processors, web servers, database, and a “match aggregator” did not change the “focus” of the asserted claims. Instead, such generic computer components were merely limitations to a particular environment, which did not make the claims any less abstract for the Alice/Mayo Step 1.
With regard to software-based inventions, the Alice/Mayo Step 1 inquiry “often turns on whether the claims focus on the specific asserted improvement in computer capabilities or, instead, on a process that qualifies as an abstract idea for which computers are invoked merely as a tool.” In addressing this, the court looks at the specification’s description of the “problem facing the inventor.” Here, the specification framed the inventor’s problem as how to improve existing polling systems, not how to improve computer technology. As such, the specification confirms that the invention is not directed to specific technological solutions, but rather, is directed to how to perform the abstract idea of matching based on progressive polling.
Under Alice/Mayo Step 2, the claimed use of general-purpose processors, match servers, unique identifications and/or a match aggregator is merely to implement the underlying abstract idea. The specification describes use of “conventional” processors, web servers, the Internet, etc. The court has “ruled many times” that “invocations of computers and networks that are not even arguably inventive are insufficient to pass the test of an inventive concept in the application of an abstract idea.” And, no inventive concept is found where claims merely recite “generic features” or “routine functions” to implement an underlying abstract idea.
Trinity’s Argument 1
Claim construction and fact discovery was necessary, but not done, before analyzing the asserted claims under §101.
Federal Circuit’s Response 1
“A patentee must do more than invoke a generic need for claim construction or discovery to avoid grant of a motion to dismiss under § 101. Instead, the patentee must propose a specific claim construction or identify specific facts that need development and explain why those circumstances must be resolved before the scope of the claims can be understood for § 101 purposes.”
Trinity’s Argument 2
Under Alice/Mayo Step One, the claims included an “advance over the prior art” because the prior art did not carry out matching on mobile phones, did not employ “multiple match servers” and did not employ “match aggregators.”
Federal Circuit’s Response 2
A claim to a “new” abstract idea is still an abstract idea.
Trinity’s Argument 3
Humans cannot mentally engage in the claimed process because humans could not perform “nanosecond comparisons” and aggregate “result values with huge numbers of polls and members” nor could humans select criteria using “servers, storage, identifiers, and/or thresholds.”
Federal Circuit’s Response 3
The asserted claims do not require “nanosecond comparisons” nor “huge numbers of polls and members.”
Trinity’s claims can be directed to an abstract idea even if the claims require generic computer components or require operations that a human cannot perform as quickly as a computer. Compare, for example, with Electric Power Group, where the court held the claims to be directed to an abstract idea even though a human could not detect events on an interconnected electric power grid in real time over a wide area and automatically analyze the events on that grid. Likewise, in ChargePoint (electric car charging network system), claims directed to enabling “communication over a network” were abstract ideas even though a human could not communicate over a computer network without the use of a computer.
Trinity’s Argument 4
Claims are eligible inventions directed to improvements to the functionality of a computer or to a network platform itself.
Federal Circuit’s Response 4
As described in the specification, mere generic computer components, e.g., a conventional computer system, server, web server, data processing system, processors, memory, mobile phones, mobile apps, are used. Such generic computer components merely provide a generic technical environment for performing an abstract idea. The specification does not describe the invention of swiping or improving on mobile phones. Indeed, the ‘685 patent describes the “advent of the internet and mobile phones” as allowing the establishment of a “plethora” or “mobile apps.” As such, “the specification does not support a finding that the claims are directed to a technological improvement in computer or mobile phone functionality.”
Trinity’s Argument 5
The district court failed to properly consider the comparison of selected answers against other uses “based on the unique identification” which was a “non-traditional design” that allowed for “rapid comparison and aggregation of result values even with large numbers of polls and members.”
Federal Circuit’s Response 5
Use of a “unique identifier” does not render an abstract idea any less abstract.
On the other hand, the “non-traditional design” appears to be based on use of an “in-memory, two-dimensional array” that “provides for linear speed across multiple match servers” and permits “an immediate comparison to determine if the user had the same answer to that of another user.” However, the asserted claims do not require any such in-memory, two-dimensional array.
Trinity’s Argument 6
The district court failed to properly consider the generation of a likelihood of a match “within a predetermined threshold.” Without this consideration, “there would be no limit or logic associated with the volume or type of results a user would receive.”
Federal Circuit’s Response 6
This merely addresses the kind of data analysis that the abstract idea of matching would include, namely how many answers should be the same before declaring a match. This does not change the focus of the claimed invention from the abstract idea of matching based on questioning.
Trinity’s Argument 7
There is an inventive concept under Alice/Mayo Step 2 because the claims recite steps performed in a “non-traditional system” that can “rapidly connect multiple users using progressive polling that compare[s] answers in real time based on their unique identification (ID) (and in the case of the ’685 patent employ swiping)” which “represents a significant advance over the art.”
Federal Circuit’s Response 7
These conclusory assertions are insufficient to demonstrate an inventive concept. “We disregard conclusory statements when evaluating a complaint under Rule 12(b)(6).”
Takeaways:
The evisceration of software-related inventions as abstract ideas continues. Although the court looks at the “claimed advance over the prior art” in assessing the “directed to” inquiry under Alice Step 1, conclusory assertions of advances over the prior art are insufficient to demonstrate inventive concept under Alice Step 2, at least for a 12(b)(6) motion to dismiss. It remains to be seen what type of description of an “advance over the prior art” would not be “conclusory” and satisfy the “significantly more” inquiry to be an inventive concept under Alice Step 2.
The one glimmer of hope for the patentee might have been the use of an “in-memory, two-dimensional array” that “provides for linear speed across multiple match servers.” An example of patent eligibility based on use of such logical structures can be found in Enfish. However, if the specification does not describe this use of an in-memory two-dimensional array and the “technological” improvement resulting therefrom to be the “focus” of the invention, even this feature might not be enough to survive § 101.
MERE AUTOMATION OF MANUAL PROCESSES USING GENERIC COMPUTERS DOES NOT CONSTITUTE A PATENTABLE IMPROVEMENT IN COMPUTER TECHNOLOGY
| December 6, 2022
International Business Machines Corporation v. Zillow Group, Inc., Zillow, Inc.
Decided: October 17, 2022
Hughes (author), Reyna, and Stoll (dissenting in parts)
Summary:
In 2019, IBM sued Zillow for infringement of several patents related to graphical display technology in the U.S. District Court for the Western District of Washington. Zillow filed a motion for judgment on the pleadings, arguing that the claims of IBM’s asserted patents were patent ineligible under § 101. The district court granted Zillow’s motion as to two IBM patents because they were directed to abstract ideas with no inventive concept. The Federal Circuit agreed with the district court decision and therefore, affirmed.
Details:
Two asserted IBM patents are U.S. Patent Nos. 9,158,789 (“the ’789 patent”) and 7,187,389 (“the ’389 patent”).
The ’789 patent
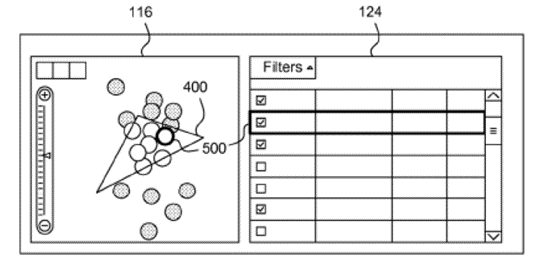
This patent describes a method for “coordinated geospatial, list-based and filter-based selection.” Here, a user draws a shape on a map to select that area of the map, and the claimed system then filters and displays data limited to that area of the map.
Claim 8 is a representative claim:
A method for coordinated geospatial and list-based mapping, the operations comprising:
presenting a map display on a display device, wherein the map display comprises elements within a viewing area of the map display, wherein the elements comprise geospatial characteristics, wherein the elements comprise selected and unselected elements;
presenting a list display on the display device, wherein the list display comprises a customizable list comprising the elements from the map display;
receiving a user input drawing a selection area in the viewing area of the map display, wherein the selection area is a user determined shape, wherein the selection area is smaller than the viewing area of the map display, wherein the viewing area comprises elements that are visible within the map display and are outside the selection area;
selecting any unselected elements within the selection area in response to the user input drawing the selection area and deselecting any selected elements outside the selection area in response to the user input drawing the selection area; and
synchronizing the map display and the list display to concurrently update the selection and deselection of the elements according to the user input, the selection and deselection occurring on both the map display and the list display.
The ’389 patent
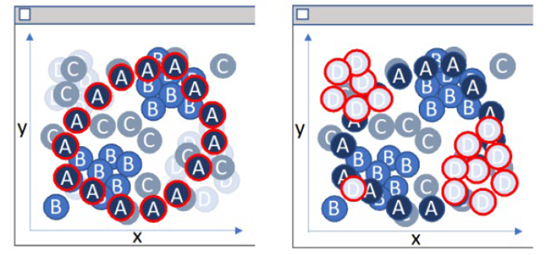
This patent describes methods of displaying layered data on a spatially oriented display based on nonspatial display attributes (i.e., displaying objects in visually distinct layers). Here, objects in layers of interest could be emphasized while other layers could be deemphasized.
Claim 1 is a representative claim:
A method of displaying layered data, said method comprising:
selecting one or more objects to be displayed in a plurality of layers;
identifying a plurality of non-spatially distinguishable display attributes, wherein one or more of the non-spatially distinguishable display attributes corresponds to each of the layers;
matching each of the objects to one of the layers;
applying the non-spatially distinguishable display attributes corresponding to the layer for each of the matched objects;
determining a layer order for the plurality of layers, wherein the layer order determines a display emphasis corresponding to the objects from the plurality of objects in the corresponding layers; and
displaying the objects with the applied non-spatially distinguishable display attributes based upon the determination, wherein the objects in a first layer from the plurality of layers are visually distinguished from the objects in the other plurality of layers based upon the non-spatially distinguishable display attributes of the first layer.
Federal Circuit
The Federal Circuit reviewed the grant of a Rule 12 motion under the law of the regional circuit (de novo for the Ninth Circuit).
As for Alice step one analysis of the ’789 patent, the Federal Circuit held that the claims fail to recite any inventive technology for improving computers as tools, and instead directed to “an abstract idea for which computers are invoked merely as a tool.”
The Federal Circuit further held that identifying, analyzing, and presenting any data to a user is not an improvement specific to computer technology, and that mere automation of manual processes using generic computers is not a patentable improvement in computer technology.
The Federal Circuit held that this patent describes functions (presenting, receiving, selecting, synchronizing) without explaining how to accomplish these functions.
As for Alice step two analysis of the ’789 patent, the Federal Circuit noted that IBM has not made any allegations that any features of the claims is inventive. Instead, the Federal Circuit held that the limitations in this patent simply describe the abstract method without providing more.
As for Alice step one analysis of the ’389 patent, the Federal Circuit agreed with the district court that this patent is directed to the abstract idea of organizing and displaying visual information (merely organize and arrange sets of visual information into layers and present the layers on a generic display device).
The Federal Circuit held that like the ’789 patent, this patent describes various functions without explaining how to accomplish any of them.
The Federal Circuit further held that the problem this patent tries to solve is not even specific to a computing environment, and the solution that this patent provides could be accomplished using colored pencils and translucent paper.
As for Alice step two analysis of the ’389 patent, the Federal Circuit noted that dynamic re-layering or rematching could also be done by hand (slowly), and that any of the patent’s improved efficiency does not come from an improvement in the computer but from applying the claimed abstract idea to a computer display.
Therefore, the Federal Circuit held that there is no inventive concept that transforms the abstract idea of organizing and displaying visual information into a patent-eligible application of that abstract idea.
Dissent by Stoll
Judge Stoll agreed with the majority opinion. However, she did not agree with the majority opinion that claims 9 and 13 of the ’389 patent are not patent eligible.
The information handling system as described in claim 8 further comprising:
a rearranging request received from a user;
rearranging logic to rearrange the displayed layers, the rearranging logic including:
re-matching logic to re-match one or more objects to a different layer from the plurality of layers;
application logic to apply the non-spatially distinguishable display attributes corresponding to the different layer to the one or more re-matched objects; and
display logic to display the one or more rematched objects.
She noted that in combination with factual allegations in the complaint (problems with the conventional technology with larger and complex data systems) and the expert declaration, the claimed relaying and rematching steps are directed to a technical improvement in how a user interacts with a computer with the GUI.
Takeaway:
- The argument that the claimed invention improves a user’s experience while using a generic computer is not sufficient to render the claims patent eligible at Alice step one analysis.
- Identifying, analyzing, and presenting certain data to a user is not an improvement specific to computing technology itself (mere automation of manual processes using generic computers not sufficient).
- The specification should be drafted to explain how to accomplish the required functions instead of merely describing them (avoid “result-based functional language”).
Tags: 35 U.S.C. §101 > Alice > patent eligible subject matter > patent ineligible subject matter
CAFC finds broadly claimed computer memory system eligible under first step of Alice.
| September 21, 2017
Visual Memory LLC v Nvidia Corporation
August 15, 2017
Before O’Malley, Hughes and Stoll. Precedential Opinion by Stoll, joined by O’Malley; Dissent by Hughes.
Summary:
Visual Memory sued Nvidia for infringement of USP 5,953,740 (the ‘740 patent). The district court granted Nvidia’s motion to dismiss for failure to state a claim (rule 12(b)(6)) based on patent ineligible subject matter. The CAFC reversed and remanded finding that the computer memory systems claims of the ‘740 satisfied the first step of Alice.
Tags: 35 U.S.C. § 101 > Alice > patent eligible subject matter > patent ineligible subject matter
Software can make non-abstract improvements to computer technology under 35 USC §101
| June 24, 2016
Enfish, LLC v Microsoft Corp.
May 12, 2016
Precedential Opinion by Hughes, joined by Moore and Taranto.
Summary:
Enfish sued Microsoft for infringement of several patents related to a “self-referential” table for a database. The district court found all claims invalid as ineligible under § 101 on summary judgment. The CAFC reversed the summary judgment based on § 101 by finding that claims drawn to a “self-referential” table for a data base are not directed to an abstract idea under step one of the Alice analysis.
Tags: 35 U.S.C. § 101 > abstract idea > Alice > eligible subject matter > ineligible subject matter
Surviving Alice Gone Wild
| November 26, 2014
Before the Supreme Court’s decision in Alice Corp. v CLS Bank Int’l [1], Judge Moore said “this case is the death of hundreds of thousands of patents, including all business method, financial system, and software patents as well as many computer implemented and telecommunications patents.”[2] This concern is premised on about twenty years of patent practice grounded in the en banc 1994 Federal Circuit decision in In re Alappat which previously established the “special purpose computer” justification for patent eligibility under 35 USC §101 for computer-implemented inventions.[3] The Alice decision essentially eliminated the “special purpose computer” bright line rule as applied generally to computer-implemented inventions. The new Mayo 2-part §101 test for computer-implemented inventions is, however, fraught with issues from the lack of guidance on how to properly apply it. Some strategic arguments for surviving a §101 attack are presented in this article, as well as a new way to address what is “significantly more.”
Tags: 101 > abstract idea > Alice > CLS Bank > computer > means plus function > patent eligible subject matter > preemption > Section 101 > software
The Alice in Wonderland En Banc Decision by the Federal Circuit in CLS Bank v. Alice
| May 13, 2013
CLS Bank v. Alice Corporation (en banc)May 10, 2013
After the Federal Circuit issued its en banc decision on May 10, 2013 in CLS Bank v. Alice Corp, the patent owner Alice Corp must be feeling like Alice in Alice in Wonderland, bewildered and frightened by the fantastical situation in which they find themselves:
(1) “bewildered” because an equally divided Federal Circuit affirmed the district court’s holding that Alice’s claimed system to tangible machine components including a first party device, a data storage unit, a second party device, a computer, and a communications controller, programmed with specialized functions consistent with detailed algorithms disclosed in the patent, constitutes a patent ineligible “abstract idea;”
(2) “frightened” because, as Judge Moore puts it, “this case is the death of hundreds of thousands of patents, including all business method, financial system, and software patents as well as many computer implemented and telecommunications patents” (Moore Op. at 2); and
(3) “fantastical” because, as Judge Newman puts it, the en banc court was tasked to provide objective standards for 35 USC §101 patent-eligibility, but instead has “propounded at least three incompatible standards, devoid of consensus, serving to add to the unreliability and cost of the [patent] system…[such that] the only assurance is that any successful innovation is likely to be challenged in opportunistic litigation, whose result will depend on the random selection of the panel” (Newman Op. at 1-2).
Tags: §101 > 101 > abstract ideas > Alice > CLS Bank > computer patents > patent eligibility > patentable subject matter > preemption > software patents