Nexus for Secondary Considerations requires Coextensiveness between a product and the claimed invention
| June 26, 2020
Fox Factory, Inc. v. SRAM, LLC
May 18, 2020
Lourie, Mayer and Wallach. Opinion by Lourie.
Summary:
SRAM sued Fox Factory for infringing U.S. Patent 9,291,250 (the ‘250 patent) and the parent patent U.S. Patent 9,182,027 (the ‘027 patent) to bicycle chainrings having teeth that alternate between widened teeth that better fit a gap between outer plates of a chain and narrower teeth to fit a gap between inner plates of a chain. Fox Factory filed IPRs against each patent. SRAM provided evidence of secondary considerations and argued that a greater than 80% gap-filling feature of the X-Sync chainring was crucial to its success for solving chain retention problem. The PTAB held that both patents are not unpatentable as obvious relying in part on secondary consideration evidence provided by SRAM. On appeal, the CAFC vacated the PTAB’s decision with regard to the ‘027 patent because the SRAM X-Sync chainring is not coextensive with the claims of the ‘027 patent that do not recite the greater than 80% gap-filling feature. However, the CAFC affirmed the PTAB’s decision for the ‘250 patent because the claims include the greater than 80% gap-filling feature.
Details:
The ’250 patent and the ‘027 patent are to bicycle chainrings. Some figures of the patents are provided below.
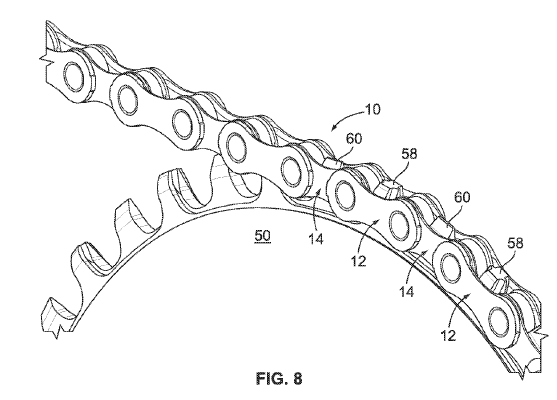
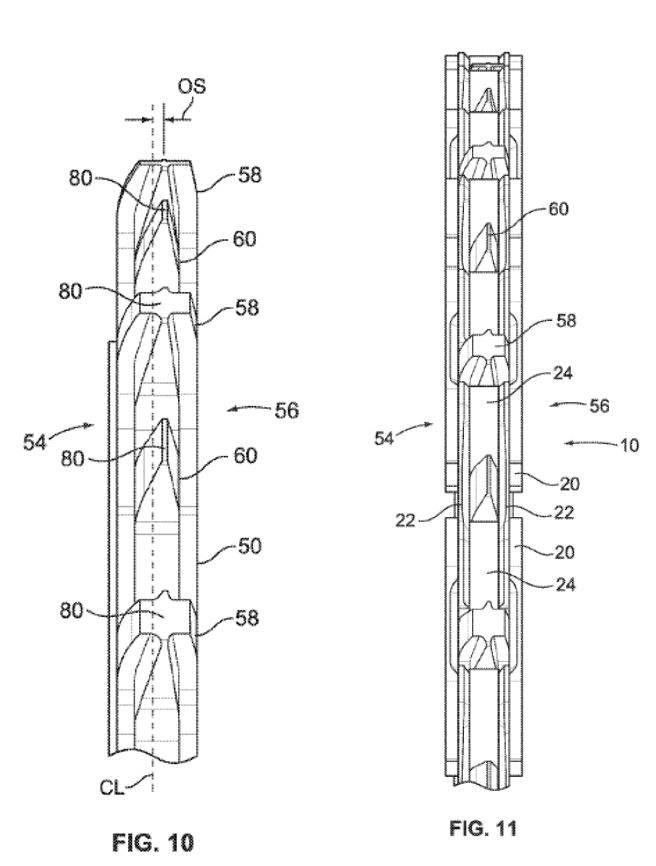
This chainring is designed to be a solitary chainring that does not need to switch between different size chainrings. Since it is a solitary chainring, the chainring can be designed to provide a tighter fit with the chain. A conventional chain has links that are alternatingly narrow and wide, but the conventional chainring has teeth that are all the same size. SRAM designed a chairing to have alternating teeth having widened teeth to fit the wide gaps and narrow teeth to fit the narrower gaps. SRAM’s product the X-Sync chainring that implements this design has been praised for its chain retention.
Claim 1 of the ‘250 patent is provided:
1. A bicycle chainring of a bicycle crankset for engagement with a drive chain, comprising:
a plurality of teeth extending from a periphery of the chainring wherein roots of the plurality of teeth are disposed adjacent the periphery of the chainring;
the plurality of teeth including a first group of teeth and a second group of teeth, each of the first group of teeth wider than each of the second group of teeth; and
at least some of the second group of teeth arranged alternatingly and adjacently between the first group of teeth,
wherein the drive chain is a roller drive chain including alternating outer and inner chain links defining outer and inner link spaces, respectively;
wherein each of the first group of teeth is sized and shaped to fit within one of the outer link spaces and each of the second group of teeth is sized and shaped to fit within one of the inner link spaces; and
wherein a maximum axial width about halfway between a root circle and a top land of the first group of teeth fills at least 80 percent of an axial distance defined by the outer link spaces.
In the IPR for the ‘250 patent, Fox Factory cited JP S56-42489 to Shimano and U.S. Patent 3,375,022 to Hattan. Shimano teaches a bicycle chainring with widened teeth to fit into the outer chain links of a conventional chain. Hattan describes that a chainring’s teeth should fill between 74.6% and 96% of the inner chain link space. Fox Factory argued that the claims would have been obvious because one of ordinary skill in the art would have seen the utility in designing a chainring with widened teeth to improve chain retention as taught by Shimano, and one of ordinary skill in the art would have looked to Hattan’s teaching with regard to the percentage of the link space that should be filled.
The PTAB held the claims to be non-obvious because of the axial fill limitation “at the midpoint of the teeth.” The PTAB found that Hattan taught the fill percentage at the bottom of the tooth instead of at the midpoint. The PTAB also found that SRAM’s evidence of secondary considerations rebutted Fox Factory’s arguments of obviousness.
On appeal, Fox Factory argued that the only difference between the prior art and the claimed invention is that the fill limitation is measured halfway up the tooth. Regarding secondary considerations, Fox Factory argued that a nexus between the claimed invention and the evidence of success of the X-Sync chainring was not demonstrated because the success is due to other various unclaimed aspects of the X-Sync chainring.
The CAFC stated that Fox Factory is correct that “a mere change in proportion … involves no more than mechanical skill, rather than the level of invention required by 35 U.S.C. § 103.” However, the CAFC stated that the PTAB “found that SRAM’s optimization of the X-Sync chainring’s teeth, as claimed in the ‘250 patent, displayed significant invention.” The CAFC pointed out that SRAM provided evidence that the success of the X-Sync chainring surprised skilled artisans, evidence of industry skepticism and subsequent praise, and evidence of a long-felt need to solve chain retention problems. The X-Sync chainring also won an award for “Innovation of the Year.” Based on the evidence, the CAFC stated that the PTAB did not err in concluding that the evidence of secondary considerations defeated the contention of routine optimization.
Fox Factory argued that the CAFC’s previous decision on the ‘027 patent requires vacatur in this case. In the appeal of the IPR for the ‘027 patent the CAFC stated that the PTAB misapplied the legal requirement of showing a nexus between evidence of secondary considerations and the obviousness of the claims of the patent. The CAFC stated that the patent owner must show that “the product from which the secondary considerations arose is coextensive with the claimed invention.” In the IPR for the ‘250 patent, SRAM argued that the greater than 80% gap-filling feature of the X-Sync chainring was crucial to its success. But the claims of the ‘027 patent do not include this greater than 80% gap filling feature. Thus, in the ‘027 appeal, the CAFC stated that no reasonable factfinder could decide that the X-Sync chainring was coextensive with a claim that did not include the greater than 80% gap filling feature, and vacated the decision of the PTAB.
In this case, the CAFC pointed out that the claims of the ‘250 patent include the greater than 80% gap filling feature, and thus, the X-Sync chainring is coextensive with the claims. The CAFC also stated that the unclaimed features relied on by Fox Factory as contributing to the success are to some extent incorporated into the 80% gap-filling feature. Thus, the CAFC found that substantial evidence supports the PTAB’s findings on secondary considerations and nexus, and the CAFC stated that they agree with the PTAB’s conclusion that the claims of the ‘250 patent would not have been obvious.
Comments
When arguing secondary considerations, make sure that there is nexus between the evidence and the claims. Specifically, you need to make sure that the product from which the secondary considerations arose is “coextensive” with the claimed invention. A product that falls within the scope of the claim is not necessarily coextensive with the claim.
This case is also a reminder to include claims having varying scope. In this case, SRAM’s claims survived because of the 80% gap-filling feature which was not included in the claims of the parent patent.


