District court’s construction of a toothbrush claim gets flossed
| January 14, 2021
Maxill Inc. v. Loops, LLC (non-precedential)
December 31, 2020
Before Moore, Bryson, and Chen (Opinion by Chen).
Summary
Construing a claim reciting an assembly of identifiably separate components, the Federal Circuit determines that a limitation associated with a claimed component pertains to the component before it is combined with the other components. The lower court’s summary judgment of non-infringement, based on a claim construction requiring assembly, is reversed.
Details
Loops, LLC and Loops Flexbrush, LLC (“Loops”) own U.S. Patent No. 8,448,285. The 285 patent is directed to a flexible toothbrush that is safe for distribution in correctional and mental health facilities. The toothbrush being made of flexible elastomers is less likely to be fashioned into a shiv.
Claim 1 of the 285 patent is representative and is reproduced below:
A toothbrush, comprising:
an elongated body being flexible throughout the elongated body and comprising a first material and having a head portion and a handle portion;
a head comprising a second material, wherein the head is disposed in and molded to the head portion of the elongated body; and
a plurality of bristles extending from the head forming a bristle brush,
wherein the first material is less rigid than the second material.
Maxill, Inc. makes “Supermaxx Prison/Institutional” toothbrushes that have a rubber-based, flexible body.

Loops and Maxill have for years been embroiled in patent infringement litigation, both in the U.S. and abroad, over flexible toothbrushes. This appeal arose out of a district court declaratory judgment action initiated by Maxill, who sought declaratory judgment of non-infringement and invalidity of the 285 patent.
During the district court proceeding, Loops moved for summary judgment of infringement. In their opposition, Maxill argued that whereas the “flexible throughout” limitation in the 285 patent claims required that the body of the toothbrush be flexible from one end to the other, only the handle portion of the body of the Supermaxx toothbrush was flexible. The head portion of the toothbrush body, including the head, did not bend.
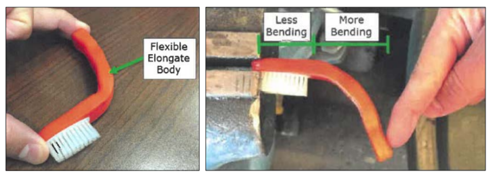
The district court agreed with Maxill, finding that Maxill’s Supermaxx toothbrush did not satisfy the “flexible throughout” limitation because the head portion of the toothbrush body, combined with the head, was rigid and unbendable. The district court then took the rare step of sua sponte granting Maxill summary judgment of non-infringement.
Loops appealed.
The main issue on appeal is the proper construction of the “flexible throughout” limitation. The question, however, is not simply whether the claim limitation requires that the body be flexible from one end to the other, but rather, whether the body must be flexible from one end to the other once assembled with the head.
As noted above, claim 1 of the 285 patent requires “an elongated body being flexible throughout the elongated body…and having a head portion and a handle portion”, and “a head…is disposed in and molded to the head portion of the elongated body”.
Does the “flexible throughout” limitation apply to the elongated body when it is combined with the head (i.e., post-assembly)? In that case, the district court was correct and Maxill’s Supermaxx toothbrush would not infringe the 285 patent.
Or does the “flexible throughout” limitation apply to the elongated body alone (i.e., pre-assembly)? In that case, the district court was wrong and Maxill’s Supermaxx toothbrush would be potentially infringing.
The Federal Circuit disagrees with the district court, determining that the “flexible throughout” limitation pertains to the elongated body alone and does not extend to the head even when the head is molded to the elongated body.
The Federal Circuit first looks at the claims, finding that the claims do not describe the head “as being a part of the elongated body; rather, the head…is identified in the claim as a separate element from the elongated body”.
Even though the claims require that the head be “disposed in and molded to” the elongated body, this recitation “does not meant that the head loses its identity as a separately identifiable component of the claimed toothbrush and somehow merges into becoming a part of the elongated body”,
The Federal Circuit then looks at the specification, finding that the specification consistently describes the head and elongated body as separate components.
Finally, the Federal Circuit finds that the prosecution history does not contain any “disclaimer requiring that the head be considered in evaluating the flexibility of the elongated body”.
The Federal Circuit is also bothered by the district court’s sua sponte summary judgment of non-infringement. This sua sponte action, says the Federal Circuit, deprived Loop of a full and fair opportunity to respond to Maxill’s non-infringement positions.
This case is interesting because the patentee seems to have accomplished a lot with (intentionally?) imprecise claim drafting. While the specification describes that the elongated body, as a standalone component, is fully flexible, there is no description that once combined with the head, the head portion of the elongated body remains flexible. But if the claims are construed the way the Federal Circuit has, written description or enablement is not an issue. And during prosecution, the patentee was able to distinguish over prior art teaching partially flexible toothbrush handles by arguing that the claimed elongated body was flexible throughout, but also distinguish over prior art disclosing toothbrushes with fully flexible handles and removable heads by arguing that the “permanent disposition of the head in the head portion is paramount in providing a fully flexible toothbrush while also providing the rigidity required in the head to effectively brush teeth”.
Takeaway
- Claim elements tend to be construed as identifiably separate components in the absence of claim language or descriptions in the specification indicating that the components are formed as a unitary whole. Take care when amending claims to add features that may exist only when the components are assembled or disassembled.
