Predictability and Criticality – Disclosure of Species Can Support Broader Genus
| August 5, 2019
IN RE: GLOBAL IP HOLDINGS LLC
July 5, 2019
Before Moore, Reyna, and Stoll
Summary
This precedential decision illustrates that disclosure of a species can support a broader genus claim. The test for sufficiency is whether the specification “reasonably conveys to those skilled in the art that the inventor had possession of the claimed subject matter as of the filing date.” Predictability and criticality are relevant to the written description inquiry.
Background
Global IP Holdings LLC (Global) filed a reissue application seeking to broaden the claims of its U.S. Patent No. 8,690,233[1]. The reissue application sought to change the term “thermoplastic” to “plastic” in independent claims 1, 14 and 17. Claim 1 is representative:
1. A carpeted automotive vehicle load floor comprising:
a composite panel having first and second reinforced
thermoplastic skins and athermoplastic cellular core disposed between and bonded to the skins, the first skin having a top surface;a cover having top and bottom surfaces and spaced apart from the composite panel; and
a substantially continuous top covering layer bonded to the top surface of the panel and the top surface of the cover to at least partially form a carpeted load floor having a carpeted cover, wherein an intermediate portion of the top covering layer between the cover and the panel is not bonded to either the panel or the cover to form a living hinge which allows the carpeted cover to pivot between different use positions relative to the rest of the load floor.
The reissue declaration of the inventor explained that he is the inventor of over fifty U.S. patents in the field of plastic-molded products and that he was aware of the use of other plastics than thermoplastics (such as thermoset plastics) for composite panels with a cellular core.
The claims of the reissue application were rejected for failing to comply with the written description requirement of 35 U.S.C. § 112, first paragraph. The Examiner noted that the specification only describes the skins and core being formed of thermoplastic materials. Thus, the Examiner considered the change to result in new matter.
On appeal to the Patent Trademark and Appeal Board (PTAB), Global argued that “because the type of plastic used is not critical to the invention and plastics other than thermoplastics were predictable options, the disclosure of thermoplastics (species) supports the claiming of plastics (genus).” The PTAB rejected these arguments, explaining that “regardless of the predictability of results of substituting alternatives, or the actual criticality of thermoplastics in the overall invention, [Global’s] Specification, as a whole, indicates to one of ordinary skill in the art that the inventors had possession only of the skins and core comprising specifically thermoplastic.”
Discussion
The CAFC reviewed the PTAB’s legal conclusions de novo and its fact finding for substantial evidence. The CAFC found that the PTAB legally erred in its analysis. In particular, the PTAB’s finding that the specification was insufficient “regardless of the predictability of results of substituting alternatives, or actual criticality of thermoplastics in the overall invention” conflicts with Ariad Pharm., Inc. v. Eli Lilly & Co., 598 F.3d 1336, 1351 (Fed. Cir. 2010) (en banc). The CAFC explained that “the predictability of substituting generic plastics for thermoplastics in the skins and cellular cores of vehicle load floors is relevant to the written description inquiry.” In addition, criticality of an unclaimed limitation to the invention “can be relevant to the written description requirement.”
The CAFC pointed to In re Peters, 723 F.2d 891, 893–94 (Fed. Cir. 1983), in which the original claims were directed to a metal tip having a tapered shape. In a reissue application of that patent, the claims were amended to cover both tapered and non-tapered tips. The Board held that the broadened claims were not supported because the original disclosure only disclosed tapered tips. The CAFC disagreed, explaining that:
“[t]he broadened claims merely omit an unnecessary limitation that had restricted one element of the invention to the exact and non-critical shape disclosed in the original patent.” Id. We reasoned that the disclosed tip configuration was not critical because no prior art was overcome based on the tip shape and “one skilled in the art would readily understand that in practicing the invention it is unimportant whether the tips are tapered.”
Accordingly, the decision of the PTAB is vacated and remanded to address the relevant factors including predictability and criticality in order to determine whether the written description requirement has been satisfied.
Takeaways
Although a specification may not literally disclose a broader genus, disclosure of a species may support a broader genus, depending on the predictability and criticality of the feature.
Could Global seek an even broader claim by deleting “thermoplastic” in its entirety? Perhaps so, if deletion of thermoplastic is considered not critical to overcome prior art as in In re Peters. A review of the patent does show use of generic terms of “skin” and “cellular core” (column 5, lines 1-26 for example).
[1] A review of the file history shows that 15 patents issued from the same priority application no. 13/453,201.
Plausible and specific factual allegations of inventive claims are enough to survive a motion to dismiss for Patent Ineligible Subject Matter
| July 22, 2019
Cellspin Soft, Inc. v. Fitbit, Inc.
June 25, 2019
Lourie, O’Malley, and Taranto
Summary:
Cellspin sued Fitbit and nine other defendants for infringement of various claims of four different patents relating to connecting a data capture device such as a digital camera to a mobile device. Fitbit filed a motion to dismiss under Rule 12(b)(6) because the asserted claims of all of the patents are to patent ineligible subject matter under § 101. The district court granted the motion to dismiss and Cellspin appealed to the CAFC. The CAFC agreed with the district court that the claims recite an abstract idea under step one of the Alice test. However, under step two of the Alice test, the CAFC stated that Cellspin made “specific, plausible factual allegations about why aspects of its claimed inventions were not conventional,” and that “the district court erred by not accepting those allegations as true.” Thus, the CAFC vacated the district court decision and remanded.
Details:
Cellspin sued Fitbit and nine other defendants for infringement of several claims of four different patents. The four patents are U.S. Patent Nos. 8,738,794; 8,892,752; 9,258,698; and 9,749,847. These patents share the same specification and relate to connecting a data capture device such as a digital camera, to a mobile device so that a user can automatically publish content from the data capture device to a website.
According to the ‘794 patent, prior art devices had to transfer their content from the digital capture device to a personal computer using a memory stick or cable. The ‘794 patent teaches using a short-range wireless communication protocol such as bluetooth to automatically or with minimal user intervention transfer and upload data from a data capture device to a mobile device. The mobile device can then automatically or with minimal user intervention publish the content on websites.
Claim 1 of the ‘794 patent recites:
1. A method for acquiring and transferring data from a Bluetooth enabled data capture device to one or more web services via a Bluetooth enabled mobile device, the method comprising:
providing a software module on the Bluetooth enabled data capture device;
providing a software module on the Bluetooth enabled mobile device;
establishing a paired connection between the Bluetooth enabled data capture device and the Bluetooth enabled mobile device;
acquiring new data in the Bluetooth enabled data capture device, wherein new data is data acquired after the paired connection is established;
detecting and signaling the new data for transfer to the Bluetooth enabled mobile device, wherein detecting and signaling the new data for transfer comprises:
determining the existence of new data for transfer, by the software module on the Bluetooth enabled data capture device; and
sending a data signal to the Bluetooth enabled mobile device, corresponding to existence of new data, by the software module on the Bluetooth enabled data capture device automatically, over the established paired Bluetooth connection, wherein the software module on the Bluetooth enabled mobile device listens for the data signal sent from the Bluetooth enabled data capture device, wherein if permitted by the software module on the Bluetooth enabled data capture device, the data signal sent to the Bluetooth enabled mobile device comprises a data signal and one or more portions of the new data;
transferring the new data from the Bluetooth enabled data capture device to the Bluetooth enabled mobile device automatically over the paired Bluetooth connection by the software module on the Bluetooth enabled data capture device;
receiving, at the Bluetooth enabled mobile device, the new data from the Bluetooth enabled data capture device;
applying, using the software module on the Bluetooth enabled mobile device, a user identifier to the new data for each destination web service, wherein each user identifier uniquely identifies a particular user of the web service;
transferring the new data received by the Bluetooth enabled mobile device along with a user identifier to the one or more web services, using the software module on the Bluetooth enabled mobile device;
receiving, at the one or more web services, the new data and user identifier from the Bluetooth enabled mobile device, wherein the one or more web services receive the transferred new data corresponding to a user identifier; and
making available, at the one or more web services, the new data received from the Bluetooth enabled mobile device for public or private consumption over the internet, wherein one or more portions of the new data correspond to a particular user identifier.
The opinion highlighted as relevant that claim 1 requires establishing a paired connection between the data capture device and the mobile device before data is transmitted between the two. The other claims from the other patents recite small variations of claim 1 of the ‘794 patent.
Nine defendants filed a motion to dismiss under Federal Rule of Civil Procedure 12(b)(6) and one defendant filed a motion to dismiss under Federal Rule of Civil Procedure 12(c). The motions argued that the asserted patents are ineligible under § 101. The district court granted the motions to dismiss stating that all of the asserted claims from all of the asserted patents are to ineligible subject matter under § 101.
CAFC – Step One Analysis
Cellspin argued that the claims are directed to improving internet-capable data capture devices and mobile networks and that its claims recite technological improvements because the claims describe improving data capture devices by allowing even “internet-incapable” capture devices to transfer newly captured data to the internet via an internet capable mobile device.
The CAFC characterized the claims as “drawn to the idea of capturing and transmitting data from one device to another.” And the CAFC stated that they have “consistently held that similar claims reciting the collection, transfer, and publishing of data are directed to an abstract idea,” and that these cases “compel the conclusion that the asserted claims are directed to an abstract idea as well.” The CAFC further stated that the patents acknowledge that users could already transfer data from a data capture device (even an internet-incapable device) to a website using a cable connected to a PC, and that the patents provided a way to automate this transfer. Thus, the CAFC concluded that the district court correctly held that the asserted claims are to an abstract idea.
CAFC – Step Two Analysis
Cellspin argued that the claimed invention was unconventional. They described the prior art devices as including a capture device with built-in wireless internet, but that these devices were inferior because at the time of the patent priority date, these combined devices were bulky, expensive in terms of hardware and expensive in terms of requiring an extra or separate cellular service for the data capture device. Cellspin stated that its device was unconventional in that it separated the steps of capturing and publishing the data by separate devices linked by a wireless, paired connection. This invention allowed for the data capture device to serve one core function of capturing data without the need to incorporate other hardware and software components for storing data and publishing on the internet. And one mobile device with one data plan can be used to control several data capture devices.
Cellspin further argued that its specific ordered combination of elements was inventive because Cellspin’s claimed device requires establishing a paired connection between the mobile device and the data capture device before data is transmitted, whereas the prior art data capture device forwarded data to a mobile device as captured regardless of whether the mobile device is capable of receiving the data, i.e. whether the mobile device is on and whether the mobile device is near the data capture device. Cellspin also argued that its use of HTTP transfers of data received over a paired connection to web services was non-existent prior to its invention.
The district court stated that Cellspin failed to cite support in the patent specifications for its allegations regarding the inventive concepts and benefits of its invention. However, the CAFC stated that in the Aatrix case (Aatrix Software Inc. v. Green Shades Software, Inc., 882 F.3d 1121 (Fed. Cir. 2018)), they repeatedly cited allegations in the complaint to conclude that the disputed claims were potentially inventive. The CAFC stated:
While we do not read Aatrix to say that any allegation about inventiveness, wholly divorced from the claims or the specification, defeats a motion to dismiss, plausible and specific factual allegations that aspects of the claims are inventive are sufficient. Id. As long as what makes the claims inventive is recited by the claims, the specification need not expressly list all the reasons why this claimed structure is unconventional.
The CAFC stated that in this case, Cellspin made “specific, plausible factual allegations about why aspects of its claimed inventions were not conventional,” and that “the district court erred by not accepting those allegations as true.”
The district court also did not give weight to Cellspins’ allegations because Cellspin relied on Berkheimer (Berkheimer v. HP Inc., 881 F.3d 1360 (Fed. Cir. 2018)), which was distinguished by the district court because the Berkheimer case dealt with a motion for summary judgment. But the CAFC stated that the district court’s conclusion cannot be reconciled with the Aatrix case and stated:
The district court thus further erred by ignoring the principle, implicit in Berkheimer and explicit in Aatrix, that factual disputes about whether an aspect of the claims is inventive may preclude dismissal at the pleadings stage under § 101.
The CAFC further stated that Cellspin did more than just label certain techniques as inventive; Cellspin pointed to evidence suggesting that these techniques had not been implemented in the same way. The CAFC concluded that Cellspin sufficiently alleged that they claimed significantly more than the idea of capturing, transferring or publishing data, and thus the district court erred by granting the motion to dismiss.
Attorney Fees
The CAFC also commented on the district court’s decision to award attorney fees to the defendant. The district court awarded attorney fees to the defendants because the district court deemed the case exceptional due to actions by Cellspin. But since the CAFC found that the district court erred in granting the motions to dismiss, the CAFC vacated the award of attorney fees. But the CAFC went further to point out errors by the district court in determining the case to be exceptional.
The CAFC faulted the district court for not presuming that the issued patents are eligible. The CAFC stated that issued patents are not only presumed to be valid but also presumed to be patent eligible. In citing Berkheimer, the CAFC stated that underlying facts regarding whether a claim element or combination is well-understood or routine must be proven by clear and convincing evidence.
Comments
A patent owner as a plaintiff in an infringement suit can defend against a motion to dismiss by providing “specific, plausible factual allegations” about why aspects of the claimed invention were not conventional. Explicit description in the specification providing reasons why the claimed invention is unconventional is not required as long as the claim recites what makes the claim inventive. Also, this case states that underlying facts regarding ineligibility must be proven by clear and convincing evidence.
Even though this case states that explicit description in the specification regarding why the invention is unconventional is not required, patent applicants should consider including a description in the specification regarding why the invention or certain aspects of the invention are unconventional to make their patents stronger.
The Federal Circuit Affirms PTAB’s Obvious Determination Against German-Based Non-Practicing Entity, Papst Licensing GMBH & Co., Based on Both Issue Preclusion and Lack of Merit
| July 19, 2019
Papst Licensing GMBH & Co. v. Samsung
May 23, 2019
Dyk, Taranto, and Chen. Opinion by Taranto
Summary
German-based non-practicing entity Papst Licensing GMBH & Co. is the owner of U.S. Patent No. 9,189,437 entitled “Analog Data Generating and Processing Device Having a Multi-Use Automatic Processor.” The ‘437 patent issued in 2015 and claims priority to an original application filed in 1999 through continuation applications, and is one of a family of at least seven patents based on the same specification and/or priority that have been asserted in litigations by Papst against various entities to seek licenses. Here, Samsung successfully brought an Inter Parties Review (IPR) proceeding before the Patent & Trademark Appeal Board (PTAB) in which the PTAB held that claims of the ‘437 were invalid as obvious over prior art. Papst appealed the PTAB’s decision, and, on appeal, the Federal Circuit affirmed the PTAB’s decision based on both issue preclusion and obviousness.
Details
Procedural Background
German-based non-practicing entity Papst Licensing GMBH & Co. (“Papst”)
is the owner of U.S. Patent No. 9,189,437 entitled “Analog Data Generating and
Processing Device Having a Multi-Use Automatic Processor.” The ‘437 patent issued in 2015 and claims
priority to an original application filed in 1999 through continuation
applications, and is one of a family of at least seven patents based on the same
specification and/or priority that have been asserted in litigations by Papst
against various companies to seek licenses.
In response to such litigations, various combinations of companies filed
numerous petitions for Inter Partes Review (IPR) to review many claims of the
family of patents. In this case,
Samsung successfully initiated an IPR proceeding before the Patent &
Trademark Appeal Board (PTAB) in which the PTAB held that claims of the ‘437
were invalid as obvious over prior art.
Factual Background
The patent at issue on appeal is U.S. Patent No. 9,189,437 is entitled “Analog Data Generating and Processing Device Having a Multi-Use Automatic Processor.” The specification describes an interface device for communication between a data device (on one side of the interface) and a host computer (on the other). The interface device achieves high data transfer rates, without the need for a user-installed driver specific to the interface device, by using fast drivers that are already standard on the host computer for data transfer, such as a hard-drive driver. In short, the interface device sends signals to the host device that the interface device is an input/output device for which the host already has such a driver – i.e., such that the host device perceives the interface device to actually be that other input/output device.
For reference, claim 1of the ‘437 patent is shown below:
1. An analog data generating and processing de-vice (ADGPD), comprising:
an input/output (i/o) port;
a program memory;
a data storage memory;
a processor operatively interfaced with the i/o port, the program memory and the data storage memory;
wherein the processor is adapted to implement a data generation process by which analog data is acquired from each respective analog acquisition channel of a plurality of independent analog acquisition channels, the analog data from each respective channel is digitized, coupled into the processor, and is processed by the processor, and the processed and digitized analog data is stored in the data storage memory as at least one file of digitized analog data;
wherein the processor also is adapted to be involved in an automatic recognition process of a host computer in which, when the i/o port is operatively interfaced with a multi-purpose interface of the host computer, the processor executes at least one instruction set stored in the program memory and thereby causes at least one parameter identifying the analog data generating and processing device, independent of analog data source, as a digital storage device instead of an analog data generating and processing device to be automatically sent through the i/o port and to the multi-purpose interface of the computer (a) without requiring any end user to load any software onto the computer at any time and (b) without requiring any end user to interact with the computer to set up a file system in the ADGPD at any time, wherein the at least one parameter is consistent with the ADGPD being responsive to commands is-sued from a customary device driver;
wherein the at least one parameter provides information to the computer about file transfer characteristics of the ADGPD; and
wherein the processor is further adapted to be involved in an automatic file transfer process in which, when the i/o port is operatively interfaced with the multi-purpose interface of the computer, and after the at least one parameter has been sent from the i/o port to the multi-purpose interface of the computer, the processor executes at least one other instruction set stored in the program memory to thereby cause the at least one file of digitized analog data acquired from at least one of the plurality of analog acquisition channels to be transferred to the computer using the customary device driver for the digital storage device while causing the analog data generating and processing device to appear to the computer as if it were the digital storage device without requiring any user-loaded file transfer enabling software to be loaded on or in-stalled in the computer at any time.
a. The Board’s IPR Decision Related to the ‘437 Patent
Before the PTAB, the board held that the relevant claims of the ‘437 – claims 1-38 and 43-45 – were invalid as obvious over U.S. Patent No. 5,758,081 (Aytac), a publication setting forth standards for SCSI interfaces (discussed in the ‘081 patent) and “admitted” prior art described in the ‘437 patent.
The Aytac patent describes connecting a personal computer to an interface device that would in turn connect to (and switch between) various other devices, such as a scanner, fax machine, or telephone. The interface device includes the “CaTbox,” which is connected to a PC via SCSI cable, and to a telecommunications switch.
In its determination of obviousness, the Board adopted a claim construction that is central to Papst’s appeal. In particular, claim 1 of the ‘437 patent requires an automatic recognition process to occur “without requiring any end user to load any software onto the computer at any time” and an automatic file transfer process to occur “without requiring any user-loaded file transfer enabling software to be loaded on or installed in the computer at any time.”
The Board interpreted the “without requiring” limitations to mean “without requiring the end user to install or load specific drivers or software for the ADGPD beyond that included in the operating system, BIOS, or drivers for a multi-purpose interface or SCSI interface.” In adopting that construction, among those that can be required to be installed for the processes to occur, relying on the specification and claims as making clear that the invention contemplates use of SCSI drivers to carry out the processes.
The Board also rejected Papst’s contention that “the ‘without requiring’ limitations prohibit an end user from installing or loading other drivers.”
b. The Board’s IPR Decision Related to the ‘144 Patent
With respect to another U.S. Patent in Papst’s family of patents – i.e., U.S. Patent No. 8,966,144, which is based on the same specification as the ‘437 patent – the PTAB had issued a similar IPR decision, in which the same claim limitations of “without requiring …” were similarly interpreted as in the present board decision and in which the claim limitation was similarly found to be obvious over the same prior art as applied in the present board decision.
Following the PTAB decision related
to the ‘144 patent, Papst appealed the decision to the Federal Circuit. However, on the eve before oral arguments,
Papst voluntarily dismissed its appeal, whereby the PTAB’s decision related to
the ‘144 patent became final.
Discussion
On appeal, the Federal Circuit affirmed the PTAB’s decision based on both issue preclusion and obviousness.
- Issue Preclusion
The Federal Circuit explained that “[t]he Supreme Court has made clear that, under specified conditions, a tribunal’s resolution of an issue that is only one part of an ultimate legal claim can preclude the loser on that issue from later contesting, or continuing to contest, the same issue in a separate case. Thus:
subject to certain well-known exceptions, the general rule is that “[w]hen an issue of fact or law is actually litigated and determined by a valid and final judgment, and the determination is essential to the judgment, the determination is conclusive in a subsequent action between the parties, whether on the same or a different claim.”
The Federal Circuit noted that “we have held that the same is true of an IPR proceeding before the Patent Trial and Appeal Board, so that the issue preclusion doctrine can apply in this court to the Patent Trial and Appeal Board’s decision in an IPR once it becomes final.”
The well-known exception, noted by the Federal Circuit, involved that: the court recognizes that “[i]ssue preclusion may be in-apt if ‘the amount in controversy in the first action [was] so small in relation to the amount in controversy in the second that preclusion would be plainly unfair.”
However, the Federal Circuit emphasized that that was not the case here, and, the court also emphasized that, in the ‘144 case Papst even brought the litigation through to the eve of oral argument, which highlights that that was not the case. Notably, the Federal Circuit also emphasizes that: “More generally, given the heavy burdens that Papst placed on its adversaries, the Board, and this court by waiting so long to abandon defense of the ’144 patent and ’746 patent claims, Papst’s course of action leaves it without a meaningful basis to argue for systemic efficiencies as a possible reason for an exception to issue preclusion.”
With respect to issue preclusion, the Federal Circuit explained that the Board in the ’144 patent decisionresolved the same claim construction issue in the same way as the Board in the present IPR. It characterized “the issue in dispute” as “center[ing] on whether the ‘without requiring’ limitations prohibit an end user from installing or loading other drivers.” Moreover, the Federal Circuit also explained that “the Board also ruled that use of SCSI software does not violate the ‘without requiring’ limitations, because the patent clearly showed that such software may be used,” and that “[t]hat ruling was not just materially identical to the Board’s claim construction ruling in this case; it also was essential to the Board’s ultimate determination, which depended on finding that the installation of CATSYNC, as disclosed in Aytac, was not prohibited by the ’144 patent’s “without requiring” limitation and that Aytac taught that the transfer process could be performed with SCSI software.”
Thus, the Federal Circuit held that issue preclusion applied in this case related to the ‘437 patent.
- Obviousness
On appeal, Papst presents two arguments that are addressed by the Federal Circuit First, Papst argues that the board improperly construed the limitation “without requiring” as meaning that the claimed processes can take place with SCSI software (or other multi-purpose interface soft-ware or software included in the operating system or BIOS).. Second, Papst argues that the board improperly concluded that Aytac teaches an automatic file transfer that can take place with only the SCSI drivers, without the assistance of user-added CATSYNC software.
With respect to the obviousness evaluation, the Federal Circuit found the Board’s conclusion regarding the construction of the “without requiring” limitations of the ‘437 patent to be correct based on the “ordinary meaning” of the words employed. The Federal Circuit explained that “[t]o state that a process can take place “without requiring” a particular action or component is, by the words’ ordinary meaning as confirmed in Celsis In Vitro, to state simply that the process can occur even though the action or component is not present; it is not to forbid the presence of the particular action or component.”
In addition, the Federal Circuit also agreed with the Board’s conclusion that SCSI interface software was permitted software in the claim construction because of the description in the specification of the ‘437 patent. The Federal Circuit expressed that: “The specification is decisive. Reflecting the recognition that SCSI interfaces were ‘present on most host devices or laptops’ at the time” and that “the specification explains that the invention contemplates use of SCSI software.”
Moreover, the Federal Circuit agreed that the “Board’s finding that a relevant skilled artisan would understand that the Aytac’s CaTbox can perform an automatic file transfer using SCSI without the CATSYNC software that Papst says is required, ” noting that Samsung’s expert Dr. Reynolds testified that only the SCSI protocol and the ASPI drivers are needed to transfer a file in Aytac, similar to the function of the ’437 patent.
Thus, the Federal Circuit affirmed the board’s determinations of obviousness related to the ‘437 patent.
Takeaway
When asserting patent infringement of multiple similar patents in a patent family, there is an increased risk of facing issue preclusion issues.
There is a Standing to Defend Your Expired Patent Even If an Infringement Suit Has Been Settled
| July 8, 2019
Sony Corp. v. Iancu
Summary:
The CAFC vacated the PTAB’s decision, in which the PTAB found that the limitation “reproducing means” is not computer-implemented and does not require an algorithm because this limitation should have been construed as computer-implemented and that the corresponding structure is a synthesizer and controller that performs the algorithm described in the specification. In addition, the CAFC found that there is a standing to appeal to defend an expired patent because the CAFC’s decision would have a consequence on any infringement that took place during the life of the patent.
Details:
Sony is the owner of U.S. Patent No. 6,097,676 (“the ’676 patent”) and appeals the PTAB’s decision in IPR, in which the PTAB found claims 5 and 8 of the ’676 patent unpatentable as obvious.
The ’676 patent:
The ’676 patent is directed to an information recording medium that can store audio data having multiple channels and a reproducing device that can select which channel to play based on a default code or value stored in a memory. This reproducing device has (1) storing means for storing the audio information, (2) reading means for reading codes associated with the audio information, and (3) reproducing means for reproducing the audio information based on the default code or value.
Claim 5 of the ’676 patent recites:
5. An information reproducing device for reproducing an information recording medium in which audio data of plural channels are multiplexedly recorded, the information reproducing device comprising:
storing means for storing a default value for designating one of the plural channels to be reproduced; and
reproducing means for reproducing the audio data of the channel designated by the default value stored in the storing means; and
wherein a plurality of voice data, each voice data having similar contents translated into different languages are multiplexedly recorded as audio data of plural channels; and a default value for designating the voice data corresponding to one of the different languages is stored in the storing means.
Claim 8 recites the same features as claim 5 with some additional features.
The PTAB:
The PTAB instituted IPR as to claims 5 and 8 of the ’676 patent. The issue during IPR was whether the “reproducing means” was computer-implemented and required an algorithm.
On September, 2017, the PTAB issued a final decision, where the claims were found to be unpatentable as obvious over the Yoshio reference. The PTAB construed the “reproducing means” has a means-plus-function limitation, and found that its corresponding structure is a controller and a synthesizer, or the equivalents. Furthermore, the PTAB found that this limitation is not computer-implemented and does not require an algorithm because a controller and a synthesizer are hardware elements.
The CAFC:
The CAFC agreed with Sony’s argument that the “reproducing means” requires an algorithm to carry out the claimed function.
The CAFC held that:
“In cases involving a computer-implemented invention in which the inventor has invoked means-plus-function claiming, this court has consistently required that the structure disclosed in the specification be more than simply a general purpose computer or microprocessor.” Aristocrat Techs. Austl. Pty Ltd. v. Int’l Game Tech., 521 F.3d 1328, 1333 (Fed. Cir. 2008). For means-plus-function claims “in which the disclosed structure is a computer, or microprocessor, programmed to carry out an algorithm,” we have held that “the disclosed structure is not the general purpose computer, but rather the special purpose computer programmed to perform the disclosed algorithm.” WMS Gaming, Inc. v. Int’l Game Tech., 184 F.3d 1339, 1349 (Fed. Cir. 1999).
The specification of the ’676 patent discloses that “[i]n reproducing such a recording medium by using the reproducing device of the present invention, the processing as shown in FIG. 16 is executed.” In fact, Fig. 16 discloses an algorithm in the form of a flowchart.
Therefore, the CAFC held that the “reproducing means” of claims 5 and 8 of the ’676 patent should be construed as computer-implemented and that the corresponding structure is a synthesizer and controller that performs the algorithm described in the specification.
Accordingly, the CAFC vacated the PTAB’s decision and remand for further consideration of whether the Yoshio reference discloses a synthesizer and controller that performs the algorithm described in the specification, or equivalent, and whether the claims would have been obvious over the Yoshio reference.
Standing to Appeal:
The ’676 patent was expired in August 2017. Petitioners have elected not to participate in the appeal before the CAFC. The parties have settled the district court infringement suit involving this patent.
Is there a standing to appeal?
Majority: YES because
- The parties to this appeal remain adverse and none has suggested the lack of an Article III case or controversy.
- The PTO argues that the PTAB’s decision should be affirmed.
- Sony argues that the PTAB’s decision should be reversed and the claims should be patentable.
- The CAFC’s decision would have a consequence on any infringement that took place during the life of the ’676 patent (past damages subject to the 6-year limitation and the owner of an expired patent can license the rights or transfer title to an expired patent).
Dissenting: NO because
- No private and public interest (patent expired, petitioner declined to defend its victory, and infringement suit has been settled).
- No hint or possibility of present or future case or controversy by both parties and the PTO.
Takeaway:
- Even if the patent has expired, the patentee has a standing to appeal before the CAFC to dispute the PTAB’s final decision.
- An algorithm described in the specification for means-plus-function language helped the patentee with a narrow claim construction.
Tags: 112(f) > case or controversy > expired patent > hardware > infringement > means-plus-function > software > standing to appeal
Satisfying Written Description When Therapeutic Effectiveness is Claimed
| June 26, 2019
Nuvo Pharmaceuticals v. Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories
Summary
The CAFC reversed and dismissed a holding by the District Court that the claims of the ‘907 and the ‘285 patents had adequate written description regarding the efficacy of an uncoated PPI. The CAFC states that it not necessary to prove that a claimed pharmaceutical compound actually achieves a certain result. However, if the claim recites said result, then there must be sufficient support in the specification. Herein, the claims were held invalid because the therapeutic effectiveness of uncoated PPI, which was recited in the claims, was not supported by the specification.
Details
The use of a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (hereinafter “NSAID”), such as aspirin, can cause gastrointestinal problems, and thus, some patients are prescribed an acid inhibitor, such as proton pump inhibitor (PPI), to be taken with said NSAID. However, even this combination therapy may be problematic. That is, if the PPI has not taken affect before the administration of the NSAID then gastrointestinal problems may still occur.
The U.S. Patent Nos. 6,926,907 (hereinafter “the ‘907 patent”) and 8,557,285 (hereinafter “the ’285 patent”) are directed towards a coordinated release drug formulation comprising an acid inhibitor/PPI and a NSAID. The coordinated release drug allows for an acid inhibitor to work before the release of the NSAID and thereby minimizes potential gastrointestinal problems. The ‘285 patent is a related patent of the ‘907 patent and both share a specification. Claim 1 of the ‘907 patent and claim 1 of the ‘285 patent are presented below:
Claim 1 of the ’907 patent:
1. A pharmaceutical composition in unit dosage form suitable for oral administration to a patient, comprising:
(a) an acid inhibitor present in an amount effective to raise the gastric pH of said patient to at least 3.5 upon the administration of one or more of said unit dosage forms;
(b) a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) in an amount effective to reduce or eliminate pain or inflammation in said patient upon administration of one or more of said unit dosage forms;
and wherein said unit dosage form provides for coordinated release such that:
i) said NSAID is surrounded by a coating that, upon ingestion of said unit dosage form by said patient, prevents the release of essentially any NSAID from said dosage form unless the pH of the surrounding medium is 3.5 or higher;
ii) at least a portion of said acid inhibitor is not surrounded by an enteric coating and, upon ingestion of said unit dosage form by said patient, is released regardless of whether the pH of the surrounding medium is below 3.5 or above 3.5.
(emphasis added)
Claim 1 of the ’285 patent:
1. A pharmaceutical composition in unit dosage form comprising therapeutically effective amounts of:
(a) esomeprazole, wherein at least a portion of said esomeprazole is not surrounded by an enteric coating; and
(b) naproxen surrounded by a coating that inhibits its release from said unit dosage form unless said dosage form is in a medium with a pH of 3.5 or higher;
wherein said unit dosage form provides for release of said esomeprazole such that upon introduction of said unit dosage form into a medium, at least a portion of said esomeprazole is released regardless of the pH of the medium.
(emphasis added)
Nuvo, who owns the ‘907 and ‘285 patents, make and sells Vimovo, which is the commercial embodiment of the patents. The patented drug achieves a coordinated release of the acid inhibitor and the NSAID in a single tablet. The core of the tablet is NSAID, which is coated so as to prevent its release before the pH has increased to a desired level, and an acid inhibitor, like PPI, on the outside of the coating, that actively works to increase the pH to said desired level. The PPI is uncoated. The specifications discloses methods for preparing and making the claimed drug formulations and provides examples of the structure and ingredients of the drug formulations but does not disclose any experimental data demonstrating the therapeutic effectiveness of any amount of uncoated PPI and coated NSAID in a single dosage form. Id. at 6. The specification discloses that coated PPIs avoid destruction by stomach acid but may not work quickly enough and the specification does not have any disclosure regarding the effectiveness of uncoated PPIs being able to raise pH. The inventor of the ‘907 and ‘285 patents recognized that an uncoated PPI is at greater risk of being destroyed by stomach acid, which would undermine the effectiveness of the PPI, but contemplated that uncoated PPI would allow for immediate release into a patient’s stomach and achieve an increase in pH level.
Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories, Inc., Mylan Pharmaceuticals, and Lupin Pharmaceuticals (hereinafter “the Generics”) submitted an Abbreviated New Drug Applications (ANDAs) to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration seeking approval to sell a generic version of Vimovo. Dr. Reddy’s submitted a second ANDA wherein the product would contain a small amount of uncoated NSAID on the outermost layer of the tablet, which is separate from the coated-core-NSAID.
Nuvo sued the Generics in the U.S. District Court for the District of New Jersey, in order to prevent the Generics from entering the market upon approval of the ANDAs, alleging all ANDAs products would infringe the ‘907 and ‘285 patents. The Generics stipulated to infringement, except for Dr. Reddy’s second ANDA product, and then countered that the ‘907 and ‘285 patents were invalid for obviousness, lack of enablement and inadequate written description.
The District Court granted Dr. Reddy’s motion for summary judgment of noninfringment of the ‘907 patent with regards to the second ANDA product. A bench trail was held regarding the validity of the ‘907 patent, the ‘285 patent, and whether the second ANDA product by Dr. Reddy infringed the ‘285 patent. It was concluded that the claims were not obvious over the prior art “because it was nonobvious to use a PPI to prevent NSAID-related gastric injury, and persons of ordinary skill in the art were discouraged by the prior art from using uncoated PPI and would not have reasonably expected it to work.” Id. at 8. It was also held that the claims of both patents were enabled and there was sufficient written description. The District Court held that the second ANDA by Dr. Reddy infringes the claims of the ‘285 patent.
At the District Court, the Generics argued that, “if they lose on their obviousness contention, then the claims lack written description support for the claimed effectiveness of uncoated PPI because ordinarily skilled artisans would not have expected it to work and the specification provides no experimental data or analytical reasoning showing the inventor possessed an effective uncoated PPI.” Id. at 9. Nuvo countered that “experimental data and an explanation of why an invention works are not required, the specification adequately describes using uncoated PPI, and its effectiveness is necessarily inherent in the described formulation.” Id. at 9. The District Court rejected Nuvo’s argument that effectiveness does not need to be described because effectiveness is inherent. The District Court acknowledged that the specification of the ‘907 and ‘285 patents did not describe efficacy of uncoated PPI. However, the District Court did conclude that there was sufficient written description because “the specification described the immediate release of uncoated PPI and the potential disadvantages of coated PPI, namely that enteric-coated PPI sometimes works too slowly to raise the intragastric pH. The district court did not explain why the mere disclosure of immediate release uncoated PPI, coupled with the known disadvantages of coated PPI, is relevant to the therapeutic effectiveness of uncoated PPI, which the patent itself recognized as problematic for efficacy due to its potential for destruction by stomach acid.” Id. at 10. The Generics appeal the written description ruling and Nuvo cross-appeals the District Court grant of summary judgment of noninfringement. Based solely on the written description issue regarding the claim language of “efficacy”, the CAFC reversed the appeal and dismissed the cross-appeal.
Before the CAFC, the Generics argued that the patents claim uncoated PPI that raises the gastric pH to at least 3.5, but that in view of the District Court’s holding, as part of the obviousness analysis, a skilled artisan would not have expected uncoated PPI to be effective to raise gastric pH, and that the specification of the patents fails to disclose the effectiveness of uncoated PPI. Id. at 12. Nuvo argued that “the claims do not require any particular degree of efficacy of the uncoated PPI itself, it is enough that the specification discloses making and using drug formulations containing effective amounts of PPI and NSAID, and experimental data and additional explanations demonstrating the invention works are unnecessary.” Id. at 12. The CAFC held that the District Court’s analysis does not support its conclusion of adequate written description and gave a review of the record to establish that the clear error standard has been met. “A written description finding is review for a clear error.” Id. at 11.
First, the CACF rejected Nuvo’s argument that the claims do not recite an efficacy requirement for uncoated PPI. As noted above, claim 1 of the ‘907 patent discloses “an acid inhibitor present in an amount effective to raise the gastric pH of said patient to at least 3.5” and claim 1 of the ‘285 patent discloses “therapeutically effective amounts of (a) esomeprazole….” The CAFC held that the claims of both patents require an amount of uncoated PPI effective to raise the gastric pH to at least 3.5. Id. at 14. Further, the CAFC noted that Nuvo’s argument, which is an attempt to “either recharacterizing the written description dispute or rewriting the claim language”, is being presented for the first time on appeal and is thus forfeited. The CAFC held that, before the District Court, the parties characterized that “claims require a therapeutically effective amount of uncoated PPI that would raise the gastric pH to at least 3.5”, that this understanding was “a fair reading of the claim language” and this understanding will not be altered in the appeal. Id. at 16.
Next, Nuvo argued that the expert testimony of Dr. Williams identified four portions of the specification that provided written description support. The Generics argued that the noted portions only disclose typical dosage amounts of uncoated PPI, the use of uncoated PPI in a drug formulation and did not discuss or explain efficacy of uncoated PPI. The CAFC agreed with the Generics. “We have expressly rejected the “argument that the written description requirement … is necessarily met as a matter of law because the claim language appears in ipsis verbis in the specification.” Enzo Biochem, Inc. v. GenProbe Inc., 323 F.3d 956, 968 (Fed. Cir. 2002).” Id. at 18. The CAFC noted that the case law does not requirement experimental data to establish effectiveness or an explanation of how or why a claimed composition will be effective. Id. at 18. Nevertheless, the CAFC held that the “record evidence demonstrates that a person of ordinary skill in the art would not have known or understood that uncoated PPI is effective.” Id. at 18. The CAFC held that the specification is fatally flawed since the “the specification provides nothing more than the mere claim that uncoated PPI might work, even though persons of ordinary skill in the art would not have thought it would work…. It does not demonstrate that the inventor possessed more than a mere wish or hope that uncoated PPI would work, and thus it does not demonstrate that he actually invented what he claimed: an amount of uncoated PPI that is effective to raise the gastric pH to at least 3.5” Id. at 19. The inventor’s own testimony confirms this holding. At trial, the inventor admitted “that he only had a ‘general concept of coordinated delivery with acid inhibition’ using uncoated PPI at the time he filed his first patent application.” Id. at 19.
Lastly, Nuvo argued that the written description requirement was satisfied due to the disclosure of how to make and use the claimed invention and accept that therapeutic effectiveness of uncoated PPI is a matter of inherency. Id. at 20 and 21. The Generics argued that Nuvo’s assertion did not satisfy written description but would only satisfy the enablement requirement, which is a separate and distinct requirement. Nuvo cited Alcon Research Ltd. v. Barr Laboratories, Inc., 745 F.3d 1180 (Fed. Cir. 2014) for support but the CAFC quickly dismissed this and noted that the factual circumstances of Alcon were “markedly different”. Id. at 22. In Alcon, the patent reference presented example formulations and disclosed data showing stability testing of the claimed invention. Further, the CAFC stated that only “under a narrow set circumstance” would inherency satisfy the written description requirement. Nuvo cited Allergan to support their argument that the claimed efficacy of uncoated PPI is necessarily inherent in the specification’s explicit disclosure of methods for making and using drug formulations containing uncoated PPI. The CAFC agreed with the Generics that the factual circumstances of Allergan are not applicable to the present case. In Allergan, the parties did not dispute the therapeutic efficacy of the claimed formulation and the specification in Allergan presented experimental results that established a trend in clinical effectiveness.
Based on the specific facts of certain cases, it is unnecessary to prove that a claimed pharmaceutical compound actually achieves a certain result. But when the inventor expressly claims that result, our case law provides that that result must be supported by adequate disclosure in the specification. In this case, the inventor chose to claim the therapeutic effectiveness of uncoated PPI, but he did not adequately describe the efficacy of uncoated PPI so as to demonstrate to ordinarily skilled artisans that he possessed and actually invented what he claimed. And the evidence demonstrates that a person of ordinary skill in the art reading the specification would not have otherwise recognized, based on the disclosure of a formulation containing uncoated PPI, that it would be efficacious because he or she would not have expected uncoated PPI to raise gastric pH. Under those facts, the patent claims are invalid for lack of adequate written description pursuant to § 112, ¶ 1.
(emphasis added). Id. at 24.
The CAFC holds that the ‘907 patent and the ‘285 patent invalid for lack of adequate written description with regards to the claimed effectiveness of uncoated PPI. The CAFC did not address the other issues on appeal and cross-appeal.
Takeaway
- Before
filing an application, one may consider identifying the written description support
in the specification for each individual feature of a claim
- Given the narrow set of circumstances, try not to rely upon inherency to satisfy written description
- If possible, include experimental data of drug formulations
A treatment method including an administering step based on discovery of a natural law is patentable eligible
| June 18, 2019
Endo pharmaceuticals, Et Al. v. Teva pharmaceuticals Et Al.
Summary
The Federal Circuit reversed the district court’s decision holding the claims of U.S. Patent No. 8,808,737 ineligible under 35 U.S.C. §101. The Federal Circuit held that the claims at issue are not directed to a natural law.
Details
Endo owns the ‘737 patent, entitled “method of treating pain utilizing controlled release oxymorphone pharmaceutical compositions and instruction on dosing for renal impairment.” The inventors of the ‘737 patent discovered that patients with moderately or severely impaired kidney function need less oxymorphone than usual to achieve a similar level of pain management. Accordingly, the treatment method of the ‘737 patent advantageously allows patients with renal impairment to inject less oxymorphone while still treating their pain.
More specifically, the degree of renal impairment of the subjects can be indicated by their creatinine clearance rate. The subjects may be separated into four groups based on their creatinine clearance rates:
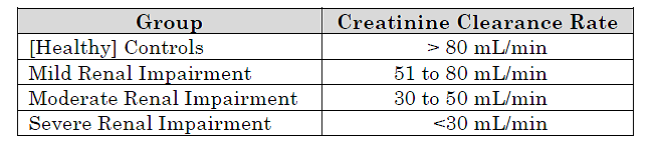
Furthermore, the inventors discover that there was a statistically significant correlation between plasma AUC (area under curve) for oxymorphone and a patient’s degree of renal impairment, as shown below:
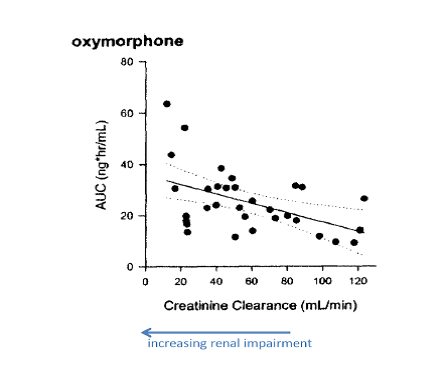
That is, there was relatively little change in oxymorphone AUC until the subjects had moderate-to-severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance rates below 50 mL/min). Subjects with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance rates below 30 mL/min) had the highest AUC values.
Claim 1 of the ‘737 patent is as follows:
1. A method of treating pain in a renally impaired patient, comprising the steps of:
a. providing a solid oral controlled release dosage form, comprising:
a) about 5 mg to about 80 mg of oxymorphone or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof as the sole active ingredient; and
b) a controlled release matrix;
b. measuring a creatinine clearance rate of the patient and determining it to be
a) less than about 30 ml/min;
b) about 30 mL/min to about 50 mL/min;
c) about 51 mL/min to about 80 mL/min, or
d) about 80 mL/min; and
c. orally administering to said patient, in dependence on which creatinine clearance rate is found, a lower dosage of the dosage form to provide pain relief;
wherein after said administration to said patient, the average AUC of oxymorphone over a 12-hour period is less than about 21 ng·hr/mL.
The magistrate judge held, and the district court agreed, that the claims at issue were not patent-eligible because the claims are directed to the natural law that the bioavailability of oxymorphone is increased in people with severe renal impairment, and the three steps a-c do not add “significant more” to qualify as a patentable method.
However, the federal circuit disagrees with the district court, holding that the claims at issue were directed to a patent-eligible application of a natural law. Specifically, The Federal Circuit points out that “it is not enough to merely identify a patent-ineligible concept underlying the claim; we must determine whether that patent-ineligible concept is what the claim is ‘directed to.’” Applying this law, the Federal Circuit concluded that claims of the ‘737 patent are directed to a patent-eligible method of using oxymorphone or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof to treat pain in a renally impaired patient. The conclusion is supported by the claim language itself and confirmed by the specification. The claim language recites specific steps a-c in using oxymorphone to treat pain in a renally impaired patient. The specification predominantly describes the invention as a treatment method, and explains that the method avoids possible issues in dosing and allows for treatment with the lowest available dose for patients with renal impairment. That is, the inventors here recognized the relationship between oxymorphone and patients with renal impairment, but claimed an application of that relationship, which is a method of treatment including specific steps to adjust or lower the oxymorphone dose for patients with renal impairment.
Then, the Federal Circuit considered that the claims at issue are similar to those in Vanda Pharmaceuticals Inc. v. West-Ward Pharmaceuticals International Ltd, (Fed. Cir. 2018) and Rapid Litig. Mgmt. Ltd. V. CellzDirect (Fed. Cir. 2016) while distinguishing the claims at issue from those in Mayo collaborative Servs. V. Prometheus Labs., Inc. (SC 2012), and Ariosa Diagnostics, Inc. v. Sequenom, Inc., (Fed. Cir. 2015). For example, the claims at issue in Vanda related to a method of treating schizophrenia patients with a drug (iloperidone), where the administered dose is adjusted based on whether or not the patient is a “CYP2D6 poor metabolizer.” Like the claims in Vanda, the claims at issue here “are directed to a specific method of treatment for specific patients using a specific compound at specific doses to achieve a specific outcome.” In contrast, the representative claim in Mayo recited administering a thiopurine drug to patient as a first step in the method before determining the natural law relationship. The administering step is not performed based on the natural law relationship, and accordingly is not an application of the natural law.
Take away
- Adding an application step such as an administering step based on discovery of a natural law will render the claims patent eligible.
- There is a potential problem of divided infringement issue here in the subsequent enforcement effort. But direct infringement against physicians and induced infringement against pharmaceutical companies have been found based on similar patent claims. Eli Lilly & Co. v. Teva Parenteral Medicines, Inc., Appeal No. 2015-2067 (Fed. Cir. Jan. 12, 2017).
More Diagnostic Patent Claims Fall—Despite following USPTO Guidelines
| May 3, 2019
Cleveland Clinic v. True Health Diagnostics
April 1, 2019
Lourie, Moore and Wallach. Opinion by Lourie. (non-precedential)
Summary
In a non-precedential opinion, the CAFC considered diagnostic patent claims ineligible. The CAFC dismissed recitation of detection of a biomarker using conventional tools as an “overly superficial” rephrasing of claims that were previously considered ineligible. The CAFC also indicated that it is not bound by USPTO guidelines, and implied that the relied-upon USPTO Example is inconsistent with Ariosa.
Details
This case relates to a diagnostic to detect heart disease. Myeloperoxidase (MPO) is an early marker of heart disease associated with atherosclerotic plaques. It was known in the prior art that MPO can be detected in surgically removed plaques, but it was not known that MPO is present in elevated levels in the blood of patients having atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. The inventors disclosed a method of detecting MPO by lab techniques such as colorimetric-based assay, flow cytometry, ELISA etc, and then correlating the detected MPO to heart disease. Notably, the specification states that MPO can be detected “by standard methods in the art,” and that commercially available kits can be modified to detect MPO.
In Cleveland Clinic I, the CAFC held that method claims reciting “a method of assessing risk of having atherosclerotic heart disease” were invalid as reciting a law of nature without anything significantly more. See Cleveland Clinic v. True Health Diagnostics LLC, 859 F.3d 1352 (Fed. Cir. 2017), cert. denied, 138 S. Ct. 2621, (2018). In that case, the claims only recited a step of “comparing” MPO levels of a subject with MPO levels in a known non-diseased person.
However, this case presents slightly different claims based on same technology. Rather than reciting diagnosis or treatment, the present claims recite methods of detecting and identifying elevated MPO, with more detail. Specifically, the relevant claims are as follows:
Patent 9,575,065:
1. A method of detecting elevated MPO mass in a patient sample comprising:
a) obtaining a plasma sample from a human patient having atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (CVD); and
b) detecting elevated MPO mass in said plasma sample, as compared to a control MPO mass level from the general population or apparently healthy subjects, by contacting said plasma sample with anti-MPO antibodies and detecting binding between MPO in said plasma sample and said anti-MPO antibodies.
Patent 9,581,597:
1. A method for identifying an elevated myeloperoxidase (MPO) concentration in a plasma sample from a human subject with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease comprising: a) contacting a sample with an anti-MPO antibody, wherein said sample is a plasma sample from a human subject having atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease;
b) spectrophotometrically detecting MPO levels in said plasma sample;
c) comparing said MPO levels in said plasma sample to a standard curve generated with known amounts of MPO to determine the MPO concentration in said sample; and
d) comparing said MPO concentration in said plasma sample from said human subject to a control MPO concentration from apparently healthy human subjects, and identifying said MPO concentration in said plasma sample from said human subject as being elevated compared to said control MPO concentration.
2. The method of claim 1, further comprising, prior to step a), centrifuging an anti-coagulated blood sample from said human subject to generate said plasma sample.
Prosecution
In prosecution of these patents, the Applicant argued by analogy to Example 29 of the May 2016 USPTO eligibility guidelines. Example 29 presents two claims:
1. A method of detecting JUL-1 in a patient, said method comprising:
a. obtaining a plasma sample from a human patient; and
b. detecting whether JUL-1 is present in the plasma sample by contacting the plasma sample with an anti-JUL-1 antibody and detecting binding between JUL-1 and the antibody.
2. A method of diagnosing julitis in a patient, said method comprising:
a. obtaining a plasma sample from a human patient;
b. detecting whether JUL-1 is present in the plasma sample by contacting the plasma sample with an anti-JUL-1 antibody and detecting binding between JUL-1 and the antibody; and
c. diagnosing the patient with julitis when the presence of JUL-1 in the plasma sample is detected.
According to the 2016 guidelines, claim 1 is eligible, because it does not recite a law of nature (pass on step 2A). However, in the USPTO’s view, claim 2 is ineligible because it recites a law of nature without reciting something significantly more (fail on steps 2A and 2B).
In prosecution, the Applicant argued that the “detecting” claim of the ‘065 patent is more similar to the “detecting” claim 1 of Example 29 (eligible) than it is to the “diagnosing” claim 2 of Example 29 (ineligible). The Examiner agreed and allowed the application.
As to the ‘597 claims, the Applicant successfully argued in prosecution that the “identifying” claim recites significantly more than a judicial exception, also relying on Example 29. The Applicant argued that it was not known to identify elevated MPO in plasma of patients having atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases, even though it was previously known to detect MPO in plaques. The Examiner agreed and allowed the application.
District Court
The district court interpreted the claims as being directed to a law of nature, based on the recitations of “detecting elevated MPO mass in a patient sample…”, “….from a human having atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease”, and “identifying an elevated [MPO] concentration in a plasma sample from a human subject with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.” The district court concluded that the method is only useful for detecting elevated MPO associated with cardiovascular disease. In other words, the method is only useful for detecting a natural phenomenon.
As such, the district court concluded that the claims do not recite a general laboratory technique and instead are trying to “recast [a] diagnostic patent as a laboratory method patent.” The district court concluded that the claims are directed to detecting the correlation between MPO and the disease, rather than to detecting MPO more generally. Thus, the claims fail step 2A. Further, the additional steps are all well-known and conventional and thus fail step 2B. Specifically, the district court stated that “[i]f merely using existing, conventional methods to observe a newly discovered natural phenomenon were enough to qualify for protection under §101, the natural law exception would be eviscerated.”
CAFC
The CAFC agreed in holding that the claims are ineligible. Cleveland Clinic argued first that the claims are not directed to a natural law, but rather to a technique of using an immunoassay to measure MPO. However, the CAFC considered this distinction to be “overly superficial,” and stated that the claims are directed to a natural law (correlation between MPO and the disease). The CAFC characterized the difference between the claims at issue and the claims of Cleveland Clinic I as a “rephrasing” that does not make the claims less directed to a law of nature.
Cleveland Clinic also argued that the correlation is not a natural law because it can only be detected using certain techniques. However, the CAFC saw through this, and stated that the same is true for many of the natural laws at issue in previous cases. Specifically, the CAFC stated that “[i]nadequate measures of detection do not render a natural law any less natural.”
The CAFC also held that the claims do not recite an additional inventive concept. Cleveland Clinic argued that using a known technique in a standard way to observe a natural law confers an inventive concept. However, the CAFC stated that this reasoning has been dismissed is previous cases such as Athena Diagnostics v. Mayo and Ariosa v. Sequenom. Further to this point, the CAFC stressed that the MPO is detected using known techniques without significant adjustments.
Finally, the CAFC addressed the USPTO guidelines. Cleveland Clinic stated that the district court erred by not giving appropriate deference to Example 29 noted above. The CAFC agreed with True Health in stating the USPTO guidelines are neither persuasive nor relevant to the claims at issue, because the district court reached the correct decision.
The CAFC did not include an extensive discussion of the USPTO guidelines, but stated as follows:
While we greatly respect the PTO’s expertise on all matters relating to patentability, including patent eligibility, we are not bound by its guidance. And, especially regarding the issue of patent eligibility and the efforts of the courts to determine the distinction between claims directed to natural laws and those directed to patent-eligible applications of those laws, we are mindful of the need for consistent application of our case law.
Further with regard to Example 29, the CAFC stated that its claim 1 is “strikingly similar” to ineligible claim 1 of Ariosa. As such, the CAFC stated that although they have considered Example 29 and related arguments, Ariosa must control. Thus, the CAFC did not follow the USPTO’s guidelines.
Takeaway
- Patent eligibility of diagnostic methods continues to be highly problematic. However, Chris Coons (D-DE) and Thom Tillis (R-NC) have recently been holding meetings on the issue, and released a “framework” on April 17, 2019:
However, in view of competing interests of the life sciences industry and the software industry, as well as reluctance to change a long-standing law, legislative change may be farther away than one might hope.
- One relies on USPTO guidelines at their own risk. Here, less than 3 years after publication, a CAFC panel has declined to follow the USPTO’s guidelines. Since such guidelines do not have the force of law, the courts are not required to follow them. In fact, in this case, the CAFC was somewhat dismissive of the USPTO’s efforts regarding §101. It is quite possible that the much-lauded USPTO guidelines issued on January 4, 2019 might suffer the same fate.
- If trying to claim a diagnostic as a detection method, it is probably better to omit recitation of a specific disease and a high/low comparison in the claims. In the rare case it is possible, it would be ideal to disclose a non-diagnostic use of the detected compound in the specification.
A comparison of an accused product to a commercial product that meets all the claim limitations for finding infringement of the claim
| April 29, 2019
TEK Global S.R.L. v. Sealant Systems International Inc. (Fed. Cir. 2019) (Prost, C.J.) (Case No. 17-2507)
March 29, 2019
Prost, Chief Judge, Dyk and Wallach, Circuit Judges. Court opinion by Chief Judge Prost.
Summary
In a precedential opinion, the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit affirmed the district court’s claim construction in a specific context that an asserted claim including “container connecting conduit” was not subject to 35 U.S.C 112, ¶ 6 (112(f)) because the term “conduit” recites sufficiently definite structure to avoid classification as a nonce term. The Federal Circuit also affirmed the district court’s overruling of the accused infringer’s objections to certain alleged product-to-product comparisons in the patentee’s closing argument with general guidance that, despite the maxim that to infringe a patent claim, an accused product must meet all the limitations of the claim, a comparison of the accused product to a commercial product that meets all the claim limitations may support a finding of infringement of the claim.
Details
I. background
1. Patent in Dispute
TEK Corporation and TEK Global, S.R.L. (collectively, “TEK”) owns U.S. Patent No. 7,789,110 (“’110 patent”), directed to an emergency kit for repairing vehicle tires deflated by puncture.
In a lawsuit by TEK against Sealant Systems International and ITW Global Tire Repair (collectively, “SSI”) at the United States District Court for the Northern District of California (“district court”), claim 26 is the only asserted independent claim:
26. A kit for inflating and repairing inflatable articles; the kit comprising a compressor assembly, a container of sealing liquid, and conduits connecting the container to the compressor assembly and to an inflatable article for repair or inflation, said kit further comprising an outer casing housing said compressor assembly and defining a seat for the container of sealing liquid, said container being housed removably in said seat, and additionally comprising a container connecting conduit connecting said container to said compressor assembly, so that the container, when housed in said seat, is maintained functionally connected to said compressor assembly, said kit further comprising an additional hose cooperating with said inflatable article; and a three-way valve input connected to said compressor assembly, and output connected to said container and to said additional hose to direct a stream of compressed air selectively to said container or to said additional hose.
2. Preceding Proceedings
In claim construction proceedings, SSI argued that “conduits connecting the container” and “container connecting conduit” in claim 26 are subject to 35 U.S.C. 112, ¶ 6, and that the claim requires a fast-fit coupling, which the accused product lacks.
FIG. 1, showing a “view in perspective of a repair kit [1] comprising a container [3] of sealing liquid [and a compressor assembly 2],” is reproduced below
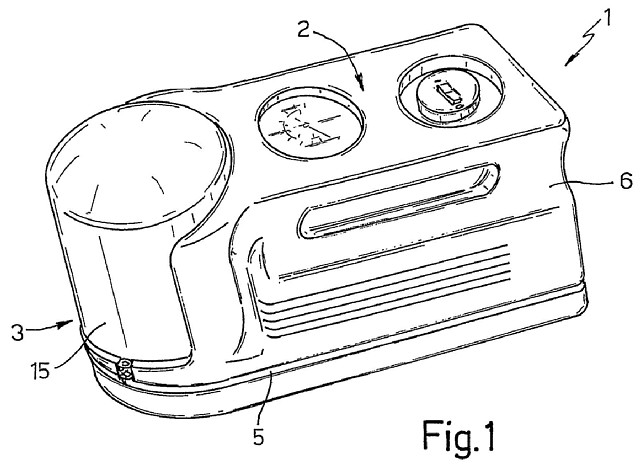
FIG. 4, showing a “underside view in perspective [o]f the FIG. 1 kit [1] partly disassembled,” and a portion of the specification of ’110 patent, relevant to the “fast-fit coupling” are reproduced below:
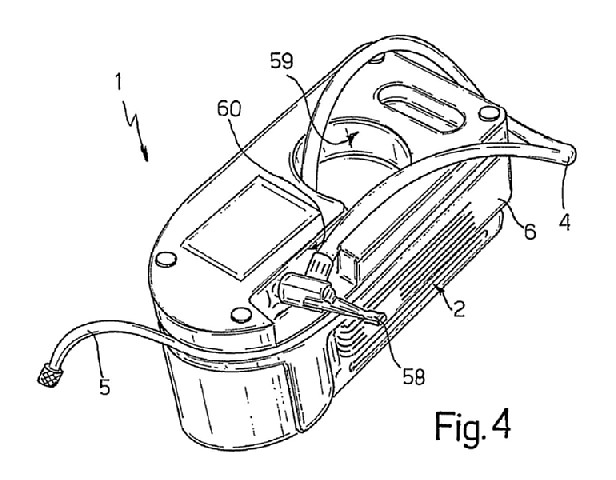
“Conveniently, hose 4 [i]s fitted on its free end with a fast-fit, e.g. lever-operated, coupling 58.” ’110 patent col. 4 ll. 7–9.
The magistrate judge rejected SSI’s contention, and entered an order respectively construing these terms (“conduits connecting the container” and “container connecting conduit”) as “hoses and associated fittings connecting the container to the compressor assembly and to an inflatable article for repair or inflation” and “a hose and associated fittings for connecting the container to the compressor assembly.”
Following the claim construction, SSI moved for summary judgment of invalidity, arguing that claim 26 was obvious over U.S. Patent Application No. 2003/0056851 (“Eriksen”) in view of Japanese Patent No. 2004-338158 (“Bridgestone”). The district court granted SSI’s motion with determinations that the term “additional hose cooperating with said inflatable article” did not require a direct connection between the additional hose and the inflatable article, and that Bridgestone discloses an air tube (54) that works together with a tire, even though it is not directly connected to the tire, and that air tube (54) therefore represents the element of an additional hose (83) cooperating with the tire. TEK appealed the district court’s order to the Federal Circuit.
The Federal Circuit reversed the district court’s construction of the “cooperating with” limitation and its subsequent invalidity determination, and remanded the case back to the district court, because SSI “has not had an opportunity to make a case for invalidity in light of this court’s claim construction.”
On remand, SSI again moved for summary judgment of invalidity, contending that “it would have been obvious . . . to modify Bridgestone to eliminate the second three-way valve (60) and joint hose (66), resulting in a conventional tire repair kit meeting the limitations of the claims of the 110 Patent.” The magistrate judge denied SSI’s motion, noting that “the Federal Circuit has already considered and rejected obviousness in light of the combination of Eriksen and Bridgestone.”
Following a four-day trial, the jury found the asserted claims including claim 26 of the ’110 patent infringed and not invalid. The jury awarded $2,525,482 in lost profits and $255,388 in the form of a reasonable royalty for infringing sales for which TEK did not prove its entitlement to lost profits.
SSI then moved for a new trial on damages (or remittitur) and for JMOL on damages, invalidity, and noninfringement. The district court denied SSI’s motions for a new trial and for JMOL on invalidity and noninfringement. As to SSI’s motion for JMOL on damages, the district court denied the motion with respect to lost profits and granted it with respect to reasonable royalty. The district court also granted TEK’s motion for a permanent injunction. SSI appealed to the Federal Circuit.
II. The Federal Circuit
The Federal Circuit vacated the district court’s final judgment as to validity and reversed its denial of SSI’s motion for partial new trial on validity. In the interest of judicial economy, the Federal Circuit also reached the remaining issues on appeal including claim construction and infringement, and affirmed on those issues in the event the ’110 patent is found not invalid following the new trial.
This article focuses on the issues of the claim construction and infringement.
1. Claim Construction
(a) Fast-fit coupling
Review the district court’s claim construction de novo, and any underlying factual findings based on extrinsic evidence for clear error, the Federal Circuit affirmed the district court’s claim construction, concluding that the intrinsic and extrinsic evidence in this case establishes that the term “conduit” recites sufficiently definite structure to avoid classification as a nonce term and agreed with the district court that SSI did not meet its burden to overcome the presumption against applying 35 U.S.C. 112, ¶ 6.
First, the Federal Circuit noted that SSI did not dispute that the elements connected via the conduits—i.e., the container, the compressor assembly, and the inflatable article (e.g., a tire)—each comprise definite structure, and that SSI did not dispute that the “hose” disclosed in the ’110 patent is structural.
Second, the Federal Circuit concluded that the ’110 patent (intrinsic evidence) clearly contemplates a conduit having physical structure. Indeed, the disclosed conduits serve to physically connect a container of sealing liquid to a compressor and to connect the compressor to tires such that “[t]he liquid is fed into the [tire] for repair by means of compressed air, e.g., by means of a compressor.” ’110 patent col. 1 ll. 13–14. Note that the cited portion in the parentheses is described in the “BACKGROUND ART” section of the specification without reference to any drawing in the patent.
Third, citing the applicant’s statement when adding new claim 26 to its patent application, “[n]ew claim 26 is similar to claim 10 but defines the connections in structural terms rather than ‘means for’ language,” the Federal Circuit agreed with the district court’s determination that the prosecution history establishes that the applicant intended for the term “conduit” to avoid the application of 35 U.S.C. 112, ¶ 6, with note that “[t]he subjective intent of the inventor when he used a particular term is of little or no probative weight in determining the scope of a claim,” but that is not necessarily true when the intent is “documented in the prosecution history.” Markman v. Westview Instruments, Inc., 52 F.3d 967, 985 (Fed. Cir. 1995) (en banc) (emphasis added).
Finally, the Federal Circuit indicated that extrinsic evidence also supports the conclusion. For example, dictionary definitions at or around the time of the invention confirm that the noun “conduit” denoted structure with “a generally understood meaning in the mechanical arts.” Greenberg v. Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Inc., 91 F.3d 1580, 1583 (Fed. Cir. 1996) (explaining that the dictionary definition of “detent” shows that a person skilled in the art would understand the term to connote structure); Webster’s Third New International Dictionary 474 (1993) (defining “conduit” as “a natural or artificial channel through which water or other fluid passes or is conveyed: aqueduct, pipe”); The New Oxford American Dictionary 358 (2001) (defining “conduit” as “a channel for conveying water or other fluid”).
(b) Outer casing connected to compressor
SSI also argues that because claim 26 requires that the “seat is part of the outer casing[,] . . . the outer casing connects the container to the compressor.”
Regarding the issue, the Federal Circuit indicated that its inquiry is limited to whether substantial evidence supports the jury’s infringement verdict under the issued claim construction, and did not reach whether the accused product infringes the asserted claims under SSI’s posited constructions because the district court expressly rejected SSI’s interpretation when determining that the term should have its plain and ordinary meaning, and because SSI did not appeal the district court’s claim construction order rejecting its interpretation of the plain and ordinary meaning.
2. Infringement (Product-to-Product Comparison)
SSI argued that the district court legally erred by allowing TEK, over SSI’s objections, to compare the accused product to TEK’s commercial embodiment during its closing argument.
While the Federal Circuit agreed with SSI’s assertion that to infringe, the accused product must meet all the limitations of the claim, the Court noted, “when a commercial product meets all the claim limitations, then a comparison [of the accused product] to that [commercial] product may support a finding of infringement.”
Regarding this case, the Federal Circuit stated that it cannot say that the district court abused its discretion by allowing the jury to hear the indirect product-to-product comparison, given that SSI’s own expert, Dr. King, acknowledged that he understood the TEK device to be an “embodying device” and to “practice[] the ’110 Patent,” and that certain statements made by SSI’s former executive, TEK’s counsel, and the inventor also suggest that TEK’s device is the commercial embodiment of the ’110 patent.
The Federal Circuit affirmed that the district court overruled SSI’s objections to certain alleged product-to-product comparisons in TEK’s closing argument because it determined that “SSI and its expert invited a product-to-product comparison by identifying TEK’s product as an embodiment of the invention, then drawing a contrast (albeit an unconvincing one) with SSI’s product.”
The Federal Circuit also affirmed that the district court, in its discretion, determined that the indirect comparison between TEK’s product and SSI’s product, in the context that it occurred, was not cause for a new trial. For the support of the affirmance, the Federal Circuit referred to the district court’s instruction directing the jury not to perform a product-to-product comparison to decide the issue of infringement (“You’ve heard evidence about both TEK’s product and SSI’s product. However, in deciding the issue of infringement, you may not compare SSI’s Accused Product to TEK’s product. Rather, you must compare SSI’s Accused Product to the claims of the ’110 Patent when making your decision regarding patent infringement.”). In the Federal Circuit’s view, the district court’s cautionary instructions are sufficient to mitigate any potential jury confusion or substantial prejudice to SSI due to the apparent product-to-product comparison.
In light of the above considerations, the Federal Circuit concluded that the district court did not abuse its discretion, and thus declined to reverse its denial of SSI’s motion for a new trial on infringement.
Takeaway
• The term “conduit” is now a member of examples of structural terms that have been found not to invoke 35 U.S.C. 112(f) or pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. 112, paragraph 6. See MPEP 2181 [R-08.2017].
• Despite the maxim that to infringe a patent claim, an accused product must meet all the limitations of the claim, a comparison of the accused product to a commercial product that meets all the claim limitations could support a finding of infringement of the claim.
A case for importing limitation from specification into the claim
| April 6, 2019
Forest Laboratories, LLC v. Sigmapharm Laboratories, LLC
March 14, 2019
Before Prost, Dyk, and Moore (Opinion by Moore)
Summary
A district court’s narrowing claim interpretation that read a limitation from the specification into the claim may have helped a patent about an antipsychotic drug survive invalidity challenges. The Federal Circuit agreed with the district court’s claim interpretation, reasoning that repeated emphasis on the limitation in the specification and prosecution history supports the reading of the limitation into the claim. The Federal Circuit also agreed that, as a solution to an unrecognized problem, the claimed invention may not be obvious, particularly when there were no alternate, independent bases on which the prior art could be combined to make the claimed invention. Unfortunately, the district court’s lack of express findings on an unrelated proffered motivation to combine prompted the Federal Circuit to nevertheless vacate the district court’s nonobviousness determination and remand the case.
Details
Forest Laboratories, LLC makes and sells the drug, SAPHRIS®, for treating bipolar disorders and schizophrenia. The active ingredient in SAPHRIS® is the compound, asenapine. This compound is the subject matter of U.S. Patent No. 5,763,476 (“476 patent”), also owned by Forest Laboratories.
SAPHRIS® on average costs almost $1,500 for 60 tablets, and there are currently no generic alternatives. When a group of drug makers sought approval from the FDA to make generic versions of SAPHRIS®, Forest Laboratories accused them of infringing the 476 patent.
For our purpose, claim 1 of the 476 patent is of particular interest:
1. A pharmaceutical composition comprising as a medicinally active compound: trans-5-chloro-2-methyl-2,3,3a,12b-tetrahydro-1H-dibenz[2,3:6,7]oxepino[4,5,-c]pyrrole or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof; wherein the composition is a solid composition and disintegrates within 30 seconds in water at 37°C.
It is worth noting that claim 4 of the 476 patent recites a “method for treating tension, excitation, anxiety, and psychotic and schizophrenic disorders, comprising administering sublingually or buccally” the asenapine.
Among the issues on appeal, the Federal Circuit’s discussions on claim construction and nonobviousness of claim 1 are informative.
As to claim construction, the question was whether claim 1 should be limited to sublingually or buccally administered compositions, or as the accused infringers would argue, should cover any composition that meets the claimed disintegration profile.
The district court determined that claim 1 should be limited to sublingual or buccal compositions. And the Federal Circuit agreed.
Unlike claim 4, claim 1 does not expressly recite “sublingual or buccal” administrations. The original claim 1 did recite “[a] sublingual or buccal pharmaceutical composition…suitable for use in sublingual or buccal compositions”, but all the “sublingual or buccal” language was removed during prosecution.
At first glance, then, the district court’s claim interpretation would seem to contradict not only the plain language of the claims, and also the intrinsic evidence vis-à-vis the prosecution history.
However, both the district court and the Federal Circuit were able to draw for their claim interpretation from the specification and prosecution history of the 476 patent.
The 476 patent specification repeatedly uses “sublingual or buccal” to modify the “invention”. For example, the 476 patent is titled “sublingual or buccal pharmaceutical composition”, and statements like “the invention relates to a sublingual or buccal pharmaceutical composition” are peppered throughout the specification. The 476 patent also extolls sublingual and buccal treatments, and criticizes conventional peroral or oral treatments.
The Federal Circuit noted that “[w]hen a patent…describes the features of the ‘present invention’ as a whole, this description limits the scope of the invention” (quoting Verizon Servs. Corp. v. Vonage Holdings Corp., 503 F.3d 1295, 1308 (Fed. Cir. 2007). In addition, both the district court and the Federal Circuit cited UltimatePointer, LLC v. Nintendo Co., 816 F.3d 816 (Fed. Cir. 2016) to support their claim interpretation. In UltimatePointer, the court limited the claim term “handheld device” to a “direct-pointing device” (for example, a Wiimote), even though the claim language did not expressly contain such a limitation. “[T]he repeated description of the invention as a direct-pointing system, the repeated extolling of the virtues of direct pointing, and the repeated criticism of indirect pointing clearly point to the conclusion that the ‘handheld device’…is limited to a direct-pointing device.” Id. at 823-24.
The prosecution history of the 476 patent likewise repeatedly used “sublingual or buccal” to modify the claimed composition. Most notably, in interpreting the original claim 1, the Examiner took the position that the language “‘suitable for sublingually or buccal administration,’ does not result in a structural difference between the claimed invention and the prior art,” and the “the composition as claimed may be used for either mode of administration (sublingually or orally, rectally, etc.).” In response, the patentee amended claim 1 to define “suitability” to mean that “the composition is a solid composition and disintegrates within 30 seconds in water at 37°C”. This feature distinguished the claimed invention over the prior art:
The Office Action indicated that any composition whose physical characteristics make the composition unique to sublingual or buccal administration…would be allowable. Applicants submit that the distinguishing feature of disintegration time is exactly such a characteristic…It is this feature of rapid disintegration which distinguishes a sublingual composition from a peroral one and which makes the compositions of the present invention suitable to avoid the adverse effects observed with peroral administration….
To obtain the good effects of the compositions of the present invention, it is necessary that the medicine be delivered by sublingual or buccal administration.
The district court inferred from those statements the inventors’ intention to limit the claims to sublingual or buccal compositions. The Federal Circuit reached the same conclusion even without considering the prosecution history. Looking only at the specification, and in a rather attenuated logic, the Federal Circuit determined that since the specification describes the claimed disintegration time as defining “rapid disintegration”, and also describes “rapid disintegration” as a feature of sublingual/buccal composition, the claimed disintegration time must therefore limit the claim to “sublingual or buccal” compositions.
Based on the above interpretation, the district court and the Federal Circuit agreed that claim 1 of the 476 patent was not obvious.
Even though asenapine, the use of asenapine to treat schizophrenia, and sublingual and buccal administrations of drugs were separately known in the art, there was no motivation to combine the prior art to arrive at the 476 patent’s sublingual or buccal formulation.
The Federal Circuit noted a “problem/solution” basis for finding nonobviousness. “[W]here a problem was not known in the art, the solution to that problem may not be obvious”. “[S]olving an unrecognized problem in the art can itself be [a] nonobvious patentable invention, even where the solution is obvious once the problem is known.”
Here, the invention grew out of concerns over severe cardiotoxic side effects of oral asenapine, which caused cardiac arrest in some patients. This prompted the inventors to consider alternative routes of administration. However, the dangers of oral asenapine were unknown in the art at the time of invention. Large-scale clinical studies were even being conducted with conventional oral asenapine tablets.
In addition, the inventors found that the cardiotoxicity of oral asenapine was likely due to accumulation of unmetabolized asenapine. However, sublingual or buccal administrations were expected to produce more, not less, unmetabolized asenapine.
The district court found, and the Federal Circuit accepted, that since nothing in the prior art indicated that oral asenapine had problems, the person skilled in the art would not have been motivated to change the route of administration. Moreover, “it would not have been predictable or expected that sublingual administration would provide a solution to the problem of cardiotoxic effect.”
The accused infringers attempted to argue, as an alternate motivation to combine, the benefit of having more treatment options. However, the Federal Circuit dismissed this argument, because “a generic need for more antipsychotic treatment options did not provide a motivation to combine these particular prior art elements.”
The Federal Circuit did disagree with the district court on one thing—unexpected results. The district court found it unexpected that sublingual administrations of asenapine lacked the cardiotoxicity of the oral formulations, because the skilled person would have expected the contrary. However, if the problem was not known, then how could the solution to the problem be “unexpected”? There would have been no expectations. As the Federal Circuit explained, “[A] person of ordinary skill could not have been surprised that the sublingual route of administration did not result in cardiotoxic effects because the person of ordinary skill would not have been aware that other routes of administration do result in cardiotoxic effect”.
The fight, however, is not completely over. The accused infringers offered a different “motivation to combine” argument, based on whether sublingual or buccal administration would have addressed patient compliance problems. The Federal Circuit did not think the district court made sufficient express findings on this proffered motivation to combine, and for this reason, vacated the district court’s nonobviousness determinations and remanded the case.
The district court and the Federal Circuit’s “problem/solution” approach to nonobviousness in this case raised an interesting question. How does that approach reconcile with the established case law that any need or problem known in the field of endeavor at the time of invention and addressed by the patent can provide a reason for combining the prior art? The whole of MPEP 2144(IV) is dedicated to explaining how the motivation to combine can be for a purpose or problem different from that of the inventor.
The Federal Circuit answered that question in a recent, non-precedential decision in In re Conrad (Fed. Cir., March 22, 2019): “[C]ases found that the inventor’s discovery of and solution to an unknown problem weighed in favor of non-obviousness because the proffered reason to modify the prior art did not present a specific, alternate basis that was unrelated to the rationale behind the inventor’s reasons for making the invention.” Where the person skilled in the art would combine the prior art “for a reason independent from solving the problem identified by [the inventor]”, the fact that the invention solved an unrecognized problem may not lend as much patentable weight as it did in Forest Laboratories.
Takeaway
In this case, the narrower interpretation worked to the patentee’s advantage, particularly because the accused infringers had already conceded on the question of infringement. But such narrowing of the claim scope after the fact may not always be desirable. One may have preserved the validity of the patent, but is left with a negligible pool of potential infringers against whom to assert the patent.
Be mindful of how the invention is defined in the specification and during prosecution. Be careful with scope-limiting language such as “The present invention is…”, and absolute language such as “necessary”, “essential”, and “the distinguishing feature”.
Question the Examiner’s rationale for combining prior art. I have on several occasions seen Examiners use “more options” to rationalize a proposed combination of prior art. This may be a cop-out, because the Examiner may not have a specific, alternate basis for combining the prior art that is unrelated to the inventor’s reasons for making the invention. In that case, the nonobviousness of the invention may be formulated as the discovery of a solution to the “recognition of an unknown problem”.
Claims to a Dietary Supplement Survive a Motion to Dismiss on a § 101 Patent Subject Matter Eligibility Challenge
| March 26, 2019
Natural Alternatives International, Inc., v. Creative Compounds, LLC
March 15, 2019
Before Moore, Reyna, and Wallach. Opinion by Moore. Opinion concurring-in-part and dissenting-in-part by Reyna.
Summary:
This case is an appeal from a Rule 12(c) dismissal for judgment on the pleadings in the district court. The district court held that all of the asserted claims to a dietary supplement, method of using the supplement and method of manufacturing the dietary supplement are patent ineligible under § 101 because they are directed to natural laws or natural phenomena. The CAFC reversed and remanded stating that the claims are not directed to an exception to § 101 under the first step of the Alice test.
Details:
Natural Alternatives sued Creative Compounds for infringement of U.S. Patent Nos. 5,965,596; 7,825,084; 7,504,376; 8,993,610; 8,470,865; and RE45,947. These patents relate to dietary supplements containing beta-alanine. Beta-alanine can form dipeptides which are also found in the muscles. Dipeptides aid in regulating intra-cellular pH during muscle contraction, and variations in concentrations of dipeptides affect anaerobic capacity. The claims of the patents are to supplements containing beta-alanine to increase the anaerobic working capacity of muscle and other tissue.
The district court accepted Natural Alternatives’ proposed claim constructions, but held that all of the claims under the proposed claim construction are patent ineligible as natural laws or natural phenomena. The CAFC stated that the district court properly accepted Natural Alternatives’ claim constructions due to the stage of the litigation, but the CAFC stated that the proposed claim constructions plausibly establish eligibility of the claims.
1. Method of Treating Claims
Claim 1 of the ‘596 patent and claim 1 of the ‘865 patent are treated as representative of the claims to a method of using beta-alanine. These claims are provided:
Claim 1 of the ‘596 patent:
1. A method of regulating hydronium ion concentrations in a human tissue comprising:
providing an amount of beta-alanine to blood or blood plasma effective to increase beta-alanylhistidine dipeptide synthesis in the human tissue; and
exposing the tissue to the blood or blood plasma, whereby the concentration of beta-alanylhistidine is increased in the human tissue.
Claim 1 of the ‘865 patent:
1. A method of increasing anaerobic working capacity in a human subject, the method comprising:
a) providing to the human subject an amount of an amino acid to blood or blood plasma effective to increase beta-alanylhistidine dipeptide synthesis in the tissue, wherein said amino acid is at least one of:
i) beta-alanine that is not part of a dipeptide, polypeptide or oligopeptide;
ii) an ester of beta-alanine that is not part of a dipeptide, polypeptide or oligopeptide; or
iii) an amide of beta-alanine that is not part of a dipeptide, polypeptide or oligopeptide; and
b) exposing the tissue to the blood or blood plasma, whereby the concentration of beta-alanylhistidine is increased in the tissue,
wherein the amino acid is provided through a dietary supplement.
Natural Alternatives’ claim construction of the highlighted “effective” limitations is to “elevate beta-alanine above natural levels to cause an increase in the synthesis of beta-alanylhistidine dipepetide in the tissue.” “Dietary supplement” is construed as “an addition to the human diet, which is not natural of conventional food, which effectively increases athletic performance when administered to the human over a period of time.” “Increasing anaerobic working capacity” is construed as “increasing the amount of work performed by a muscle under lactate producing conditions.”
The district court held that both method claims are directed to natural laws in that “ingesting certain levels of beta-alanine, will increase the carnosine concentration in human tissue and, thereby, increase the anaerobic working capacity in a human.” The CAFC disagreed with the district court stating that “[a]dministering certain quantities of beta-alanine to a human subject alters that subject’s natural state.” The CAFC stated that due to administering beta-alanine, homeostasis is overcome and the body produces more creatine which results in physiological benefits for athletes engaged in intense exercise. The CAFC also emphasized that the claims require administering the dosage form claimed in the manner claimed, altering the athlete’s physiology to provide described benefits. Citing Vanda Pharmaceuticals Inc. v. West-Ward Pharmaceuticals International Ltd., the CAFC concluded that “[t]hese are treatment claims and as such they are patent eligible.” “The Method Claims are directed to patent eligible new ways of using an existing product, beta-alanine.”
The CAFC distinguished Mayo by stating that while the Method Claims rely on a relationship between the administration of beta-alanine and beta-alanylhistidine dipeptide synthesis, under Natural Alternatives’ constructions, “the Method Claims require specific steps be taken in order to bring about a change in a subject, altering the subject’s natural state,” and the Method Claims do more than simply recite a natural law. The CAFC concluded that the Method Claims describe using a natural product in unnatural quantities to alter a patient’s natural state, to treat a patient with specific dosages. Thus, the Method Claims are not directed to an exception to § 101 under the first step of Alice.
2. Dietary Supplement Claims
Claim 6 of the ‘376 patent and claim 1 of the ‘084 patent are treated as representative of the claims to a dietary supplement. Claim 6 of the ‘376 patent depends from claims 1 and 5. The claims are provided:
Claims 1, 5 and 6 of the ‘376 Patent:
1. A composition, comprising:
glycine; and
a) an amino acid selected from the group consisting of a beta-alanine, an ester of a beta-alanine, and an amide of a beta-alanine, or
b) a di-peptide selected from the group consisting of a beta-alanine di-peptide and a beta-alanylhistidine di-peptide.
5. The composition of claim 1, wherein the composition is a dietary supplement or a sports drink.
6. The composition of claim 5, wherein the dietary supplement or sports drink is a supplement for humans.
Claim 1 of the ‘084 patent:
1. A human dietary supplement, comprising a beta-alanine in a unit dosage of between about 0.4 grams to 16 grams, wherein the supplement provides a unit dosage of beta-alanine.
Natural Alternatives construed “dietary supplement” as “an addition to the human diet, which is not a natural or conventional food, which effectively increases athletic performance and is manufactured to be used over a period of time.”
The district court held that the Product Claims are directed to the natural phenomena of beta-alanine and glycine, and thus, are directed to ineligible subject matter. The CAFC disagreed stating that the Product Claims are not directed to beta-alanine. The claims are directed to specific treatment formulations that incorporate natural products and they have different characteristics and can be used in a manner that natural beta-alanine cannot be used.
The CAFC added that beta-alanine and glycine are incorporated into particular dosage forms. The natural products are isolated and then incorporated into a dosage form with particular characteristics. In addition, the CAFC stated that “the record indicates that the claimed combination of glycine and beta-alanine could have synergistic effects allowing for outcomes that the individual components could not have.” The CAFC added that the factual allegations are sufficient to render judgment on the pleadings inappropriate, and that the Product Claims survive a motion for judgment on the pleadings at the first step of the Alice test.
3. Manufacturing Claims
Claim 1 of the ‘610 patent is treated as representative of the claims to a method of manufacturing a dietary supplement. This claim is provided:
1. Use of beta-alanine in manufacturing a human dietary supplement for oral consumption;
supplying the beta-alanine, which is not part of a dipeptide, polypeptide or oligopeptide, as a single ingredient in a manufacturing step of the human dietary supplement or
mixing the beta-alanine, which is not part of a dipeptide, polypeptide or oligopeptide, in combination with at least one other ingredient for the manufacture of the human dietary supplement,
whereby the manufactured human dietary supplement is for oral consumption of the human dietary supplement in doses over a period of time increases beta-alanyl histidine levels in muscle tissue sufficient to delay the onset of fatigue in the human.
The district court held that this claim is directed to “the natural phenomenon beta alanine and the natural law that ingesting certain levels of beta-alanine will increase the carnosine concentration in human tissue.” The CAFC disagreed stating that the claim is directed to “an application of the law and new use of that product.” The CAFC stated that the supplement is not a product of nature and the use of the supplement to achieve a given result is not directed to a law of nature, and thus, “[w]e do not see, therefore, how a claim to the manufacture of a non-natural supplement would be directed to the law of nature or natural product.” Thus, the CAFC held that the claims are not directed to ineligible subject matter under step one of the Alice test.
Dissent
Judge Reyna stated that the majority relies on an erroneous claim construction because Natural Alternatives’ claim construction improperly imports limitations into the claims. He took issue with the construction for claim 1 of the ‘084 patent. Specifically, Natural Alternatives construed “human dietary supplement” to be “an addition to the human diet, ingested as a pill, capsule, powder or liquid, which is not natural or conventional food, meat or food flavoring or extract, or pharmaceutical product which effectively increases the function of a tissue when administered to the human over a period of time.” Judge Reyna stated that this construction improperly imports the limitation that beta-alanine “effectively increases the function of a tissue when administered to the human over a period of time” because it is not in the plain language of the claim. He also stated that the proposed construction is contradicted by the written description.
Judge Reyna raised the issue of whether the court should reconsider whether a Rule 12(c) motion based on § 101 should be decided before claim construction. He interprets the majority’s remand to mean that upon formal claim construction, the § 101 issue may be revisited and asks “whether anything meaningful has been achieved in these circumstances.”
Comments
In this case, Natural Alternatives provided a favorable proposed claim construction for surviving the § 101 issue and due to the stage of the litigation at the motion to dismiss phase, the court adopted much of this proposed claim construction. Relying on this claim construction, the CAFC found all of the claims to be patent eligible. However, as Judge Reyna pointed out, it is not clear that the district court will adopt such a favorable claim construction at the claim construction stage of the litigation. And the § 101 issue might be raised again.
« Previous Page — Next Page »

