A treatment method including an administering step based on discovery of a natural law is patentable eligible
| June 18, 2019
Endo pharmaceuticals, Et Al. v. Teva pharmaceuticals Et Al.
Summary
The Federal Circuit reversed the district court’s decision holding the claims of U.S. Patent No. 8,808,737 ineligible under 35 U.S.C. §101. The Federal Circuit held that the claims at issue are not directed to a natural law.
Details
Endo owns the ‘737 patent, entitled “method of treating pain utilizing controlled release oxymorphone pharmaceutical compositions and instruction on dosing for renal impairment.” The inventors of the ‘737 patent discovered that patients with moderately or severely impaired kidney function need less oxymorphone than usual to achieve a similar level of pain management. Accordingly, the treatment method of the ‘737 patent advantageously allows patients with renal impairment to inject less oxymorphone while still treating their pain.
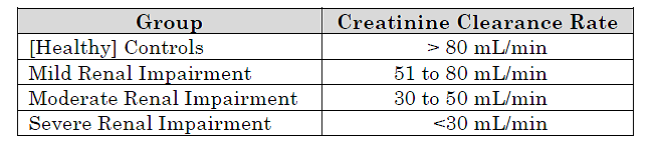
More specifically, the degree of renal impairment of the subjects can be indicated by their creatinine clearance rate. The subjects may be separated into four groups based on their creatinine clearance rates:
Furthermore, the inventors discover that there was a statistically significant correlation between plasma AUC (area under curve) for oxymorphone and a patient’s degree of renal impairment, as shown below:
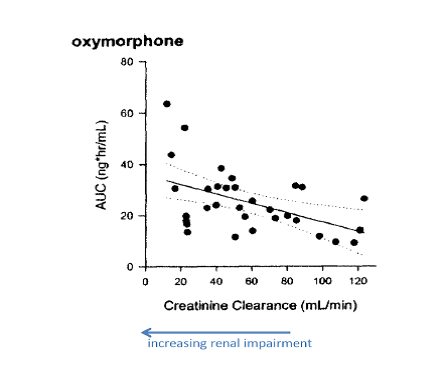
That is, there was relatively little change in oxymorphone AUC until the subjects had moderate-to-severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance rates below 50 mL/min). Subjects with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance rates below 30 mL/min) had the highest AUC values.
Claim 1 of the ‘737 patent is as follows:
1. A method of treating pain in a renally impaired patient, comprising the steps of:
a. providing a solid oral controlled release dosage form, comprising:
a) about 5 mg to about 80 mg of oxymorphone or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof as the sole active ingredient; and
b) a controlled release matrix;
b. measuring a creatinine clearance rate of the patient and determining it to be
a) less than about 30 ml/min;
b) about 30 mL/min to about 50 mL/min;
c) about 51 mL/min to about 80 mL/min, or
d) about 80 mL/min; and
c. orally administering to said patient, in dependence on which creatinine clearance rate is found, a lower dosage of the dosage form to provide pain relief;
wherein after said administration to said patient, the average AUC of oxymorphone over a 12-hour period is less than about 21 ng·hr/mL.
The magistrate judge held, and the district court agreed, that the claims at issue were not patent-eligible because the claims are directed to the natural law that the bioavailability of oxymorphone is increased in people with severe renal impairment, and the three steps a-c do not add “significant more” to qualify as a patentable method.
However, the federal circuit disagrees with the district court, holding that the claims at issue were directed to a patent-eligible application of a natural law. Specifically, The Federal Circuit points out that “it is not enough to merely identify a patent-ineligible concept underlying the claim; we must determine whether that patent-ineligible concept is what the claim is ‘directed to.’” Applying this law, the Federal Circuit concluded that claims of the ‘737 patent are directed to a patent-eligible method of using oxymorphone or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof to treat pain in a renally impaired patient. The conclusion is supported by the claim language itself and confirmed by the specification. The claim language recites specific steps a-c in using oxymorphone to treat pain in a renally impaired patient. The specification predominantly describes the invention as a treatment method, and explains that the method avoids possible issues in dosing and allows for treatment with the lowest available dose for patients with renal impairment. That is, the inventors here recognized the relationship between oxymorphone and patients with renal impairment, but claimed an application of that relationship, which is a method of treatment including specific steps to adjust or lower the oxymorphone dose for patients with renal impairment.
Then, the Federal Circuit considered that the claims at issue are similar to those in Vanda Pharmaceuticals Inc. v. West-Ward Pharmaceuticals International Ltd, (Fed. Cir. 2018) and Rapid Litig. Mgmt. Ltd. V. CellzDirect (Fed. Cir. 2016) while distinguishing the claims at issue from those in Mayo collaborative Servs. V. Prometheus Labs., Inc. (SC 2012), and Ariosa Diagnostics, Inc. v. Sequenom, Inc., (Fed. Cir. 2015). For example, the claims at issue in Vanda related to a method of treating schizophrenia patients with a drug (iloperidone), where the administered dose is adjusted based on whether or not the patient is a “CYP2D6 poor metabolizer.” Like the claims in Vanda, the claims at issue here “are directed to a specific method of treatment for specific patients using a specific compound at specific doses to achieve a specific outcome.” In contrast, the representative claim in Mayo recited administering a thiopurine drug to patient as a first step in the method before determining the natural law relationship. The administering step is not performed based on the natural law relationship, and accordingly is not an application of the natural law.
Take away
- Adding an application step such as an administering step based on discovery of a natural law will render the claims patent eligible.
- There is a potential problem of divided infringement issue here in the subsequent enforcement effort. But direct infringement against physicians and induced infringement against pharmaceutical companies have been found based on similar patent claims. Eli Lilly & Co. v. Teva Parenteral Medicines, Inc., Appeal No. 2015-2067 (Fed. Cir. Jan. 12, 2017).


