PATENT CLAIMS CANNOT BE CONSTRUED ONE WAY FOR ELIGIBILITY AND ANOTHER WAY FOR INFRINGEMENT
| September 17, 2021
Data Engine Technologies LLC v. Google LLC
Decided on August 26, 2021
Reyna, Hughes, Stoll. Opinion by Stoll.
Summary:
This case is a second appeal to the CAFC. In the first appeal, the CAFC reversed the district court and determined that certain claims of patents owned by Data Engine Technologies LLC (DET) directed to spreadsheet technologies are patent eligible subject matter. In arguing patent eligible subject matter, DET emphasized the claimed improvement as being unique to three-dimensional spreadsheets. On remand, the district court construed the preamble of the claims having the phrase “three-dimensional spreadsheet” as limiting, and based on this claim construction, granted Google’s motion for summary judgment of noninfringement. In this appeal, the CAFC affirmed the district court’s determination that the preamble of the claims is limiting and that the district court’s construction of the term “three-dimensional spreadsheet” is correct. Thus, the CAFC affirmed the district court’s summary judgment of noninfringement.
Details:
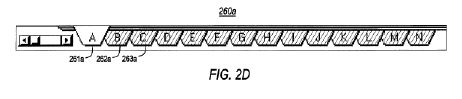
DET’s patents at issue in this case are U.S. Patent Nos. 5,590,259; 5,784,545; and 6,282,551 directed to systems and methods for displaying and navigating three-dimensional electronic spreadsheets. They describe providing “an electronic spreadsheet system including a notebook interface having a plurality of notebook pages, each of which contains a spread of information cells, or other desired page type.” Figs. 2A and 2D of the ‘259 patent are shown below. Fig. 2A shows a spreadsheet page having notebook tabs along the bottom edge. Fig. 2D shows just the notebook tabs of the spreadsheet.
Claim 12 of the ‘259 patent is a representative claim and is provided below:
12. In an electronic spreadsheet system for storing and manipulating information, a computer-implemented method of representing a three-dimensional spreadsheet on a screen display, the method comprising:
displaying on said screen display a first spreadsheet page from a plurality of spreadsheet pages, each of said spreadsheet pages comprising an array of information cells arranged in row and column format, at least some of said information cells storing user-supplied information and formulas operative on said user-supplied information, each of said information cells being uniquely identified by a spreadsheet page identifier, a column identifier, and a row identifier;
while displaying said first spreadsheet page, displaying a row of spreadsheet page identifiers along one side of said first spreadsheet page, each said spreadsheet page identifier being displayed as an image of a notebook tab on said screen display and indicating a single respective spreadsheet page, wherein at least one spreadsheet page identifier of said displayed row of spreadsheet page identifiers comprises at least one user-settable identifying character;
receiving user input for requesting display of a second spreadsheet page in response to selection with an input device of a spreadsheet page identifier for said second spreadsheet page;
in response to said receiving user input step, displaying said second spreadsheet page on said screen display in a manner so as to obscure said first spreadsheet page from display while continuing to display at least a portion of said row of spreadsheet page identifiers; and
receiving user input for entering a formula in a cell on said second spreadsheet page, said formula including a cell reference to a particular cell on another of said spreadsheet pages having a particular spreadsheet page identifier comprising at least one user-supplied identifying character, said cell reference comprising said at least one user-supplied identifying character for said particular spreadsheet page identifier together with said column identifier and said row identifier for said particular cell.
In the first appeal regarding patent eligibility, DET argued that a key aspect of the patents “was to improve the user interface by reimagining the three-dimensional electronic spreadsheet using a notebook metaphor.” DET argued that claim 12 is directed to patent-eligible subject matter because it is to a concept that solves “a problem that is unique to not only computer spreadsheet applications …., but specifically three-dimensional electronic spreadsheets.” In that appeal, the CAFC agreed that claim 12 is to patent eligible subject matter and remanded to the district court.
On remand, during claim construction, a dispute arose over whether the preamble is a limitation of the claims requiring construction, and if so, what is the proper construction of the term. The district court determined that the preamble is limiting and determined that the term “three-dimensional spreadsheet” means a “spreadsheet that defines a mathematical relation among cells on different spreadsheet pages, such that cells are arranged in a 3-D grid.” Based on this interpretation, Google moved for summary judgment of noninfringement because Google Sheets is not a “three-dimensional spreadsheet” as required by the claims. The district court granted the motion because “Google Sheets does not allow a user to define the relative position of cells in all three dimensions and is, therefore, incapable of infringing” the claims.
In this appeal, DET argued that the preamble term “three-dimensional spreadsheet” is not limiting and thus does not have patentable weight. The CAFC disagreed stating that a patentee cannot rely on language found in the preamble of the claim to successfully argue patent eligible subject matter, and then later assert that the preamble term has no patentable weight for purposes of showing infringement. The CAFC stated that “[w]e have repeatedly rejected efforts to twist claims, ‘like a nose of wax,’ in ‘one way to avoid [invalidity] and another to find infringement.’” In citing an analogous case, the CAFC stated that it cannot be argued that the preamble has no weight when the preamble was used in prosecution to distinguish prior art. In re Cruciferous Sprout Litig., 301 F.3d 1343, 1347–48 (Fed. Cir. 2002). The CAFC concluded that because DET emphasized the preamble term to support patent eligibility, the preamble term “three-dimensional spreadsheet” is limiting.
DET next argued that the construction of “three-dimensional spreadsheet” does not require “a mathematical relation among cells on different spreadsheet pages” as required by the district court’s construction. The CAFC stated that the claim language and the specification do not provide guidance on whether the mathematical relation is required. However, the CAFC looked to the prosecution history. To overcome a rejection based on a prior art reference, the applicant provided a definition of a “true” three-dimensional spreadsheet and stated that the prior art does not provide a true 3D spreadsheet. According to the applicant, a “true” three-dimensional spreadsheet “defines a mathematical relation among cells on the different pages so that operations such as grouping pages and establishing 3D ranges have meaning.” Based on this definition provided in the prosecution history, the CAFC stated that the district court properly interpreted “three-dimensional spreadsheet” as requiring a mathematical relation among cells on different spreadsheet pages.
DET argued that the definition provided in the prosecution history does not rise to the level of “clear and unmistakable” disclaimer when read in context. Specifically, DET stated in the same remarks that the prior art reference is a three-dimensional spreadsheet, and thus, could not have been distinguishing the prior art based on the three-dimensional spreadsheet feature. DET stated that they distinguished the prior art on the basis that the prior art linked different user-named spreadsheet files and that this is not the same as the claimed “user-named pages in a 3D spreadsheet.” Thus, DET argued that the statements defining a “true” 3D spreadsheet are irrelevant. However, the CAFC stated that they have held patentees to distinguishing statements made during prosecution even if they said more than needed to overcome a prior art rejection citing Saffran v. Johnson & Johnson, 712 F.3d 549, 559 (Fed. Cir. 2013). Thus, the CAFC concluded that even if the specific definition of a “true” 3D spreadsheet was not necessary to overcome the rejection, the express definition was provided, and DET cannot escape the effect of this statement made to the USPTO by suggesting that the statement was not needed to overcome the rejection. The CAFC affirmed the district court’s claim construction and its summary judgment of noninfringement.
Comments
In litigation, you will not be able to vary the construction of claims one way for validity and another way for infringement. Also, if you rely on features in the preamble of a claim for validity, the preamble will be considered as limiting and having patentable weight for infringement purposes.
Another key point from this case is that during prosecution of a patent application, you should say as little as possible to distinguish the prior art. Distinguishing statements in the prosecution history, even if not necessary to overcome the prior art, can be used to limit your claims.
The Non-Obviousness of Obviousness Determinations: Even In Simple Technologies, It Can Be Difficult to Draw a Line in Obviousness Determinations
| January 9, 2013
C.W. Zumbiel Company, Inc. v. Kappos and Graphic Packaging International, Inc.
December 27, 2012
Panel: Prost, Moore, and Wallach. Opinion by Wallach. Dissent byProst.
Summary:
This appeal arises out of an Inter Partes Reexamination before the Board of Patent Appeals and Interferences, the decision. Both the patentee and the third-party requester appealed the Board’s decision, which indicated that certain claims were obvious and certain claims were nonobvious. In this case, the Federal Circuit affirmed the Board’s entire decision. The technology at issue involved a carton for a pack of cans (such as, e.g., soda cans) having a perforated flap portion that is torn and folded down to dispensing the cans. This case highlights that even in non-complex technologies, it can be difficult to draw a line in obviousness determinations, and how when there are little possible variations in structure, if such variations lead to predictable results obviousness may be found (such as here in, e.g., claim 1), but that when there are little possible variations in structure, if other factors such as teaching away in the art, lack of incentive for such a modification exist, nonobviousness may be found (such as here in, e.g., claim 2).